Vietnam’s e-commerce sector is entering a defining period of growth. With a digital economy set to reach US$52 billion by 2025 and sustained annual growth of 29% since 2020, Vietnam has established itself as a leading e-commerce destination in Southeast Asia. This exceptional momentum, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and driven by a young, digitally fluent population, has drawn significant international attention – as demonstrated by Alibaba’s recent investment in Masan Group Corp.
For foreign investors considering Vietnam’s expanding e-commerce business, the prospects are substantial, though success requires careful preparation. The e-commerce business landscape in Vietnam presents compelling opportunities, supported by an emerging middle class and widespread internet adoption. However, investors must understand key market characteristics, from consumer behaviors – including preferences for cash-on-delivery payments and physical product inspection – to the regulatory framework governing foreign direct investment (FDI) in e-commerce business, according to Mr. Benny Nguyen, Head of Business Development at InCorp Vietnam.
This guide offers insights into establishing an e-commerce business in Vietnam for foreign investors, covering company formation, regulations (including Decree No. 52 amendments), and key success factors.
Interested in E-commerce in Vietnam? Check out InCorp Vietnam’s Incorporation Services
Types of E-Commerce Activities in Vietnam
Before launching an e-commerce business, it is vital to understand the primary business models that have proven successful in Vietnam’s digital commerce sector.
1. Online Retail Market: Retailers who operate their digital stores and manage product inventory independently. These businesses build dedicated online platforms to showcase their products, often integrating their digital presence with physical retail locations to maximize market reach.
2. Online Marketplaces: Digital platforms that connect multiple vendors with consumers under one virtual roof. These marketplaces create value by offering extensive product variety and secure transaction environments. Notable examples include homegrown platforms like Tiki and Sendo, alongside international players such as Amazon and Alibaba, each contributing to Vietnam’s diverse e-commerce ecosystem.
3. Online Classifieds: Peer-to-peer trading platforms where sellers list products directly to potential buyers. Unlike traditional marketplaces, these platforms focus on connecting parties while leaving payment and delivery arrangements to the users themselves. This model gives sellers complete control over their listings and transaction terms.
Investment Registration Procedure for an FDI Company in E-Commerce in Vietnam
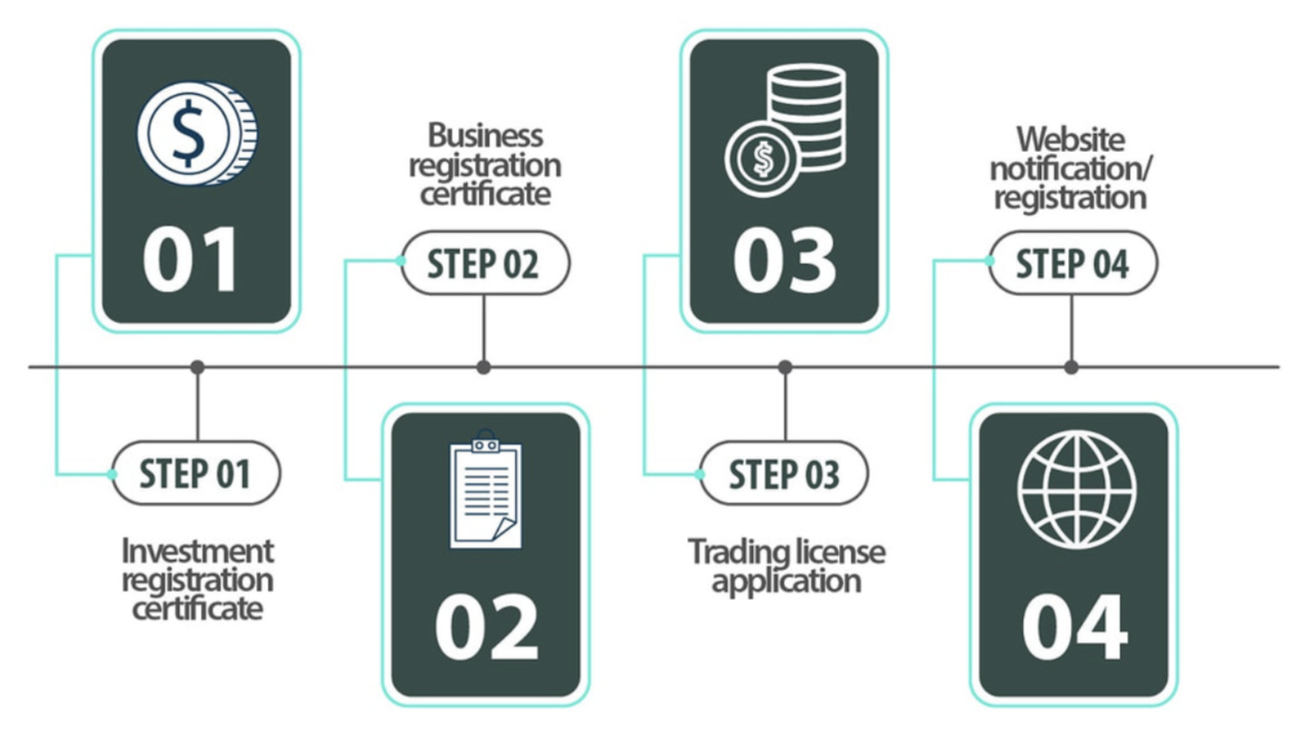
The establishment of a foreign-invested e-commerce company in Vietnam follows a structured licensing process under the 2014 Vietnam Investment Law. This process requires fulfilling specific registration procedures to obtain investment licenses, business registration certificates, and additional permits.
1. Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) Application: The initial phase requires obtaining an IRC from the Department of Planning and Investment (DPI). Investors must submit:
- Investment Project Proposal detailing the project, investment capital, and business objectives
- Notarized copies of the investor’s legal documents (passport or business registration certificate)
- Financial capacity documentation demonstrating the ability to support the business
2. Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC) Application: Upon securing the IRC, companies must obtain an ERC to establish their legal presence. Required documentation includes:
- Application Form detailing the company name, address, and charter capital.
- Company Charter outlining the organizational structure and operations.
- Documents for Founding Shareholders providing information on shareholders and their contributions.
3. E-commerce Website Registration with Ministry of Industry and Trade: The final phase involves registering the e-commerce platform through MOIT’s system:
- Step 1: Create an account in the online system by providing:
- Name of applicant
- Certificate of incorporation number
- Business lines
- The head office address of the applicant
- Contact information
- Step 2: Upon verification of adequate information, MOIT grants access to the online system. Applicants can then log on to register their e-commerce website or application and complete the required forms.
- Step 3: After MOIT approves the submission, applicants must send an original registration dossier to MOIT.
- Step 4: Upon verification, MOIT issues an official code for displaying the ‘registered’ sign on the e-commerce website or app.
Additional Requirements:
- Website Registration Compliance:
- Provide complete website information, including domain name, business activities, and management contact details.
- Ensure compliance with consumer protection regulations regarding user privacy, return policies, and secure payment systems.
- Post-Registration Requirements:
- After obtaining IRC and ERC, the FDI company must apply for additional business licenses based on their conditional activities or operations.
- Maintain ongoing compliance with relevant regulations and guidelines.
Business Licenses Required for E-Business and E-Commerce Services
For foreign investors looking to establish an e-commerce business in Vietnam, several crucial licenses and certificates are required. This guide outlines the essential business licenses and compliance requirements you will need to operate legally in the Vietnamese market.
1. Investment Registration Certificate (IRC)
The IRC serves as your official permission to invest and conduct business activities in Vietnam’s e-commerce sector. This certificate is obtained from the Ministry of Planning and Investment (MPI) in your intended province of operation.
Key Aspects of IRC Application:
- Submit a detailed business plan
- Specify investment capital
- Outline the chosen business structure
- Demonstrate compliance with Vietnamese regulations
The MPI will thoroughly review your application to ensure alignment with local regulations. Working with a Vietnamese business law specialist can help ensure a smooth approval process.
2. Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC)
After securing the IRC, you must obtain the ERC, which serves as your official business license. This certificate is issued by the Enterprise Registration Office (ERO) in the same province as your IRC.
Required Documents for ERC:
- Company Charter (including company name, purpose, management structure, and ownership details)
- Proof of physical address in Vietnam (lease agreement or ownership documents)
- Evidence of Initial Capital Contribution
- Other supporting documentation as required by local authorities
The ERC process is typically faster than the IRC application, but its importance cannot be understated as it is essential for legal operation.
3. E-Commerce Website License
All e-commerce businesses must obtain specific licenses from the Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) for their online operations. This requirement applies particularly to:
- E-commerce platforms
- Online trading floors
- E-marketplaces
- Mobile applications for e-commerce
4. Additional Industry-Specific Licenses
Depending on your business activities and products, you may need additional specialized licenses:
Product-Specific Licenses:
- Food Safety Certificate (for food products)
- Import Licenses (for imported goods)
- Special Business Licenses (for alcohol, tobacco, etc.)
Industry-Specific Requirements:
- Healthcare services licenses
- Financial services permit
- Other sector-specific authorizations
5. Compliance Requirements
Data Privacy and Security:
- Adherence to the Law on Cybersecurity
- Implementation of personal data protection measures
- Compliance with data localization requirements (storing certain data on servers in Vietnam)
- User notification protocols for data collection practices
Read Related: A Dissection of Vietnam’s Personal Data Protection Decree – Compliance Guide for Investors
Consumer Protection Standards:
- Clear communication of consumer rights and obligations
- Transparent product and service information
- Implementation of refund policies
- Establishment of dispute resolution procedures
Important Considerations
- Professional Guidance: Consider working with legal experts familiar with Vietnamese business law to ensure complete compliance and smooth license acquisition.
- Compliance Importance: Operating without required licenses can result in:
- Financial penalties
- Product seizures
- Potential business closure
- Loss of market trust
- Timeline Management: Plan for adequate time to obtain all necessary licenses and permits before commencing operations.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough records of all licenses, permits, and compliance documentation.
Remember that this licensing framework is designed to ensure responsible business practices and protect both businesses and consumers in the Vietnamese e-commerce marketplace. Proper compliance from the start will help establish a strong foundation for your e-commerce venture in Vietnam.
Read Related: Vietnam’s Personal Data Protection (PDP) Requirements: Guide to Decree 13/2023/ND-CP
Key Requirements for an FDI Company in E-Commerce in Vietnam
Foreign Ownership Structure
E-commerce services in Vietnam occupy a unique position in the country’s regulatory framework. Although these services are not explicitly defined in Vietnam’s WTO commitments on services or local regulations, this creates a favorable environment for foreign investors. The following points highlight key aspects that support this favorable environment for FDI in e-commerce:
- Neither Vietnam’s WTO Commitments nor domestic legislation explicitly restricts foreign investment in e-commerce
- The absence of specific regulations allows for flexibility in the ownership structure
- Foreign investors can establish wholly foreign-owned enterprises (100% foreign ownership) in the e-commerce sector
- No predetermined foreign ownership caps exist for e-commerce operations
Read More: The Definitive Guide to Vietnam’s 17 Active Free Trade Agreements – FTAs
Capital Requirements
Vietnamese law does not mandate a specific minimum investment capital for FDI companies engaging in e-commerce services. However, investors should note:
- Investment capital requirements are determined case-by-case, based on the project’s scope and scale
- Capital contributions can be made through multiple channels:
- Direct cash investments
- Fixed asset contributions
- A combination of both cash and fixed assets
When planning investment capital, the key consideration should be ensuring it aligns appropriately with the proposed business operations and scale of the e-commerce venture. This flexible approach allows investors to structure their investments according to their business plans while maintaining compliance with Vietnamese regulations.
Read More: An Extensive Guide to Industry Capital & Deposit Requirements in Vietnam
Legal Representative Requirements for an E-Commerce Company Organization Structure
Residency Requirements
Your company’s legal representative must maintain residential status in Vietnam, which can be established through either:
- Physical presence in Vietnam for at least 183 days per year, or
- Possession of a valid temporary residence permit
Flexibility for Foreign Representatives
Foreign nationals serving as legal representatives have additional options for managing their responsibilities:
- They can establish a power of attorney arrangement
- This allows them to fulfill their duties without requiring constant physical presence in Vietnam
Tax Obligations
Legal representatives who maintain residency in Vietnam must fulfill specific tax obligations:
- Annual income reporting to Vietnamese tax authorities
- Payment of applicable taxes on their Vietnam-sourced income
This streamlined structure allows for efficient company representation while ensuring compliance with Vietnamese regulatory requirements. The flexibility offered through power of attorney arrangements makes it practical for foreign representatives to maintain their role while managing their international commitments.
Challenges Facing E-Commerce Businesses and How InCorp Vietnam Can Assist
Vietnam’s e-commerce sector presents significant growth opportunities for foreign investors. However, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of specific challenges.
Challenges for Foreign Investors:
- Evolving Regulatory Framework: Staying abreast of frequent changes to regulations concerning data protection, tax compliance, and e-commerce licensing is essential for sustained operations. Adapting to these evolving requirements can be demanding.
- Licensing and Registration Procedures: The process of securing necessary licenses and registrations for e-commerce activities in Vietnam can be complex and time-intensive, often requiring specialized expertise.
- Data Privacy and Localization: Compliance with Vietnam’s data localization regulations and stringent consumer data protection laws is critical. Meeting these requirements necessitates robust data management strategies.
- Competitive Market Landscape: Vietnam’s e-commerce market is characterized by strong competition. Developing a differentiated market entry strategy and understanding local consumer preferences are crucial for success.
Read More: Top 10 Challenges of Doing Business in Vietnam: Notes and Advice for Foreign Investors
InCorp Vietnam: Your Strategic Partner for E-commerce Success
InCorp Vietnam, a fully licensed business consultancy, is dedicated to supporting foreign investors in navigating these challenges and achieving their e-commerce objectives in Vietnam. Our comprehensive services include:
- Facilitating 100% foreign ownership of e-commerce businesses.
- Managing all licensing and registration processes, ensuring full compliance with Vietnamese regulations.
- Providing expert guidance and support on data privacy and localization requirements.
- Developing tailored market entry strategies to address competitive dynamics and cultural nuances.
InCorp Vietnam empowers foreign investors to overcome regulatory complexities and market challenges, enabling them to capitalize on the vast opportunities within Vietnam’s e-commerce market. Request a complimentary consultation today to explore how InCorp Vietnam can facilitate your success in Vietnam.

clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly
Learn the Right Setup for Business
Expansion in the Vietnam
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 6 types of e-commerce?
- The six common types of e-commerce are: 1. **Business-to-Consumer (B2C)** – Transactions between businesses and individual consumers (e.g., online retail). 2. **Business-to-Business (B2B)** – Transactions between businesses, such as wholesale suppliers and retailers. 3. **Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)** – Transactions between consumers, often facilitated by third-party platforms (e.g., marketplaces like eBay). 4. **Consumer-to-Business (C2B)** – Individuals selling products or services to businesses (e.g., freelancers). 5. **Business-to-Government (B2G)** – Businesses providing goods or services to government agencies. 6. **Government-to-Consumer (G2C)** – Government entities offering services or information directly to citizens through digital platforms.
What is the meaning of eCommerce?
- eCommerce, or electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods or services over the internet. It includes various business models like B2B, B2C, C2C, and C2B, and involves online transactions such as payments, order processing, and customer service.






