The digital banking landscape in Vietnam is expanding rapidly, driven by high smartphone penetration and a tech-savvy population. According to Nguyen Quoc Hung, Secretary-General of the Vietnam Banks Association (VBA), technological advancements help banks streamline operations through automation, enhance productivity, improve customer service, and reduce costs.
With only 20% of Vietnam’s 90 million citizens using banking services, the underbanked population presents a major opportunity for digital banking in Vietnam. Credit card penetration is just 3%, creating significant growth potential for financial institutions.
The rise of e-commerce is fueling digital payments, with card transactions expected to surge 50%. Millennials, making up 20% of the population, are a key force behind this shift, favoring instant purchasing and digital financial solutions.
For companies looking to enter the market, Vietnam’s digital banking industry presents attractive prospects. Expert advisory and legal adherence services, backed by substantial experience in market entry, can aid in effectively launching a business in this vibrant market.
Looking to invest in Digital Banking in Vietnam? Explore InCorp Vietnam’s Market Entry Business Consulting Services
Digital Banking in Vietnam: An Overview
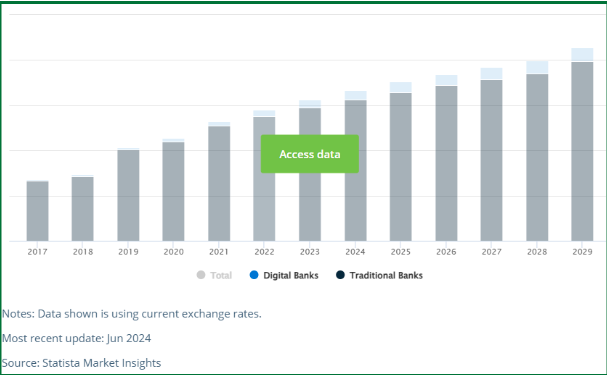
Vietnam’s digital banking sector is set for impressive expansion, with Net Interest Income expected to hit US$1.17 billion by 2025. The industry shows significant growth, predicting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.46% from 2025 to 2029, which is anticipated to elevate the market volume to US$1.56 billion by 2029. Although these numbers are striking, they are relatively modest when compared to market leaders such as China, which is expected to produce a Net Interest Income of US$528.8 billion in 2025.
The swift growth of Vietnam’s digital banking industry is mainly fueled by the rising use of smartphones and a young, tech-savvy demographic that offers favorable conditions. The nation’s initiatives for banking digitalization have produced outstanding outcomes in recent years, especially concerning non-cash transactions.
A major milestone has been reached as adult payment account ownership has hit 87%, exceeding the 2025 goal of 80% much earlier than anticipated. This accomplishment highlights the effective endeavors of banks in advancing digital financial inclusion.
The change is especially noticeable in the rapid expansion of digital payment methods. Mobile payment transactions have shown impressive year-over-year growth surpassing 100%, whereas Internet banking services have sustained a strong growth rate of 50%.
These changes have resulted in the broad acceptance of non-cash payment options, with almost 50% of the banking clientele now frequently using digital payment methods. One of the most notable signs of this digital revolution is the value of non-cash payments in 2023, which exceeded the nation’s GDP by a factor of 23, underscoring the remarkable scale and speed of digital financial change in Vietnam.
Read Related: New 2024 Law on Credit Institutions: What Foreign Investors Need to Know
Trends in Digital Banking and Mobile Banking Development
Vietnam’s digital banking environment is undergoing considerable change on both desktop and mobile platforms. The financial services industry is set for significant expansion, as the International Data Corporation (IDC) predicts that digital financial services revenue will hit US$3.8 billion by 2025. This forecast illustrates the industry’s strong growth and rising acceptance of digital technologies.
The market dynamics are notably captivating, as emerging financial institutions exhibit a higher risk tolerance than traditional banks, enabling them to penetrate critical financial services significantly. This tactical method transforms Vietnam’s banking industry’s competitive environment.
The mobile banking sector demonstrates remarkable potential, as the Fintech and Digital Banking 2025 (Asia Pacific) IDC InfoBrief anticipates a possible 300% increase in mobile transactions. This significant rise in mobile banking usage is anticipated to drive extensive changes throughout the overall digital banking landscape.
The rise in mobile transactions marks a significant shift in consumer behavior, emphasizing the growing importance of digital banking in Vietnam. As mobile-first solutions gain traction, digital advancements and accessibility are becoming essential to financial services and customer engagement.
Read Related: Blockchain 3.0 in Vietnam: Navigating the Evolving Blockchain Landscape and Logistics Opportunities
Adapting to Industry Trends in Digital Banking in Vietnam
Recent studies from the Vietnam Investment Review highlight significant progress in digital banking in Vietnam, while also identifying challenges such as engaging untapped customer segments, redefining physical branches’ roles, and addressing the gap between customers’ stated digital banking intentions and actual usage.
The digitization of banking operations offers major efficiency gains, particularly in account opening, where digital tools reduce processing time from hours to minutes. Advanced analytics enable banks to personalize offers and reach customers through preferred channels at optimal times. While digital banking in Vietnam accounts for 68% of customer interactions, most transactions involve basic functions like balance checks. More complex services, including loans, insurance, and advisory offerings, present opportunities for banks to develop tailored, high-value solutions.
With 70% of Vietnamese consumers using multiple banking channels, institutions must focus on seamless, end-to-end digital experiences. However, customer service remains a pressing issue, with 40-50% of consumers switching banks due to poor branch service, highlighting the urgent need for digital training and standardized service quality.
Read Related: The Remarkable Rise of Vietnam’s Fintech Industry: A Guide for Fintech Vietnam Investors
TPBank exemplifies a successful digital-first approach, leveraging electronic know-your-customer (eKYC) technology that enables identity verification via selfie authentication, catering to younger, tech-savvy consumers.
In the SME sector, Vietnamese banks face structural challenges despite increasing focus. Traditional banking models still prioritize secured lending and high-value collateralized loans, overlooking diverse SME needs. The reliance on commercial credit methods designed for large enterprises has created inefficiencies, while digital onboarding and service processes for small businesses remain fragmented.
The micro SME (MSME) sector faces distinct difficulties, marked by elevated operational expenses and restricted access to suitable banking services. Nevertheless, McKinsey’s analysis indicates that micro and small enterprises represent an overlooked “white space” market with considerable revenue potential, limited mainly by supply-side challenges instead of demand.
Internal Catalysts for Financial Digitalization in Vietnam
The financial digitalization landscape in Vietnam is being shaped by several key internal enablers:
- Favorable Macroeconomic and Demographic Fundamentals: Vietnam’s demographic composition presents a significant advantage with its population of 96.5 million, where 70% consists of young, digitally-native citizens. Economic projections indicate strong growth potential, with GDP per capita expected to reach US$4,449 by 2025, creating a robust foundation for digital financial services adoption.
- Advanced Consumer Digital Readiness: The market demonstrates strong digital engagement metrics, evidenced by a 66% internet penetration rate and an impressive 130% mobile subscription rate, indicating multiple device ownership per individual and highlighting the population’s technological adaptability.
- Dynamic Entrepreneurial Ecosystem: Vietnam has established itself as ASEAN’s third most vibrant startup ecosystem, following Singapore and Indonesia. This positioning reflects the country’s innovative capacity and ability to foster technological advancement in the financial sector.
- Comprehensive Digital Infrastructure: The nation’s technological backbone is characterized by extensive 4G network coverage reaching over 99% of households. Furthermore, the three primary mobile carriers have completed commercial 5G testing phases, with strategic plans to achieve 25% coverage by 2025.
- Progressive Regulatory Environment: The government demonstrates a strong commitment to digital transformation in banking and financial services through strategic initiatives. This includes the establishment of the Fintech Steering Committee, implementation of the Banking Strategy, and the introduction of Directive 16/CT-TTG, all of which create a supportive framework for digital innovation.
Conclusion: Vietnam’s Digital Banking Future
Vietnam’s digital banking scene showcases significant potential, fueled by robust technological infrastructure, a tech-savvy populace, and an encouraging regulatory environment. With traditional banks moving to digital platforms and the rapid advancement of fintech, Vietnam is positioned to emerge as a significant contender in Southeast Asia’s digital banking landscape. Through ongoing cooperation among regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers, the sector is set for ongoing growth, offering improved financial inclusion and inventive solutions for Vietnamese consumers.

clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly







