As Jack Nguyen, CEO of InCorp Vietnam, explains, “Vietnam’s Environmental Protection Tax is not just a compliance burden – it’s a wake-up call for businesses. Startups and SMEs that understand and adapt early will not only avoid penalties but also gain a competitive edge by moving toward greener, more sustainable operations.”
Understanding Vietnam Environmental Protection Tax
The Vietnam environmental protection tax (EPT) is an indirect tax levied on products and goods that are considered harmful to the environment. The aim is to incorporate the environmental cost of these items into their price, thereby disincentivizing their use and encouraging businesses and consumers to opt for greener alternatives.
Common items subject to this tax include fuels (like gasoline and diesel), coal, certain chemical substances, and particular types of plastic products. By taxing these goods, the government seeks to reduce pollution and fund environmental protection efforts using the tax revenue. This aligns with Vietnam’s broader commitment to sustainable development and its environmental goals (including a pledge to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050), although the tax’s immediate impact on businesses is more concrete in terms of compliance and cost.
From a business perspective, the environmental protection tax essentially increases the cost of producing or importing the affected goods. It is structured as a specific tax per unit of product (e.g. per liter of fuel or per kilogram of material) rather than a percentage of value. This means the tax amount is fixed for each unit of the product, providing certainty but also requiring careful tracking of quantities.
Importantly, the Vietnam environmental protection tax is typically applied only once in the supply chain – at the point of importation or production. Producers and importers are responsible for paying it upfront, and the cost is generally passed on in the price of goods down to end consumers. In summary, the tax functions both as a financial instrument to support environmental projects and as a policy tool to influence business behavior toward sustainability.
Download: A Comprehensive Checklist to Set Up A Business In Vietnam
Taxable Goods and Tax Rates under the Vietnam Environmental Protection Tax
Not all products are subject to the Vietnam environmental protection tax – it specifically targets certain categories of goods known to cause environmental harm if overused or improperly disposed of. Below is a breakdown of the key taxable goods and the applicable tax rates (current as of 2025). These rates are set in Vietnamese đồng (VND) with approximate USD equivalents for reference:
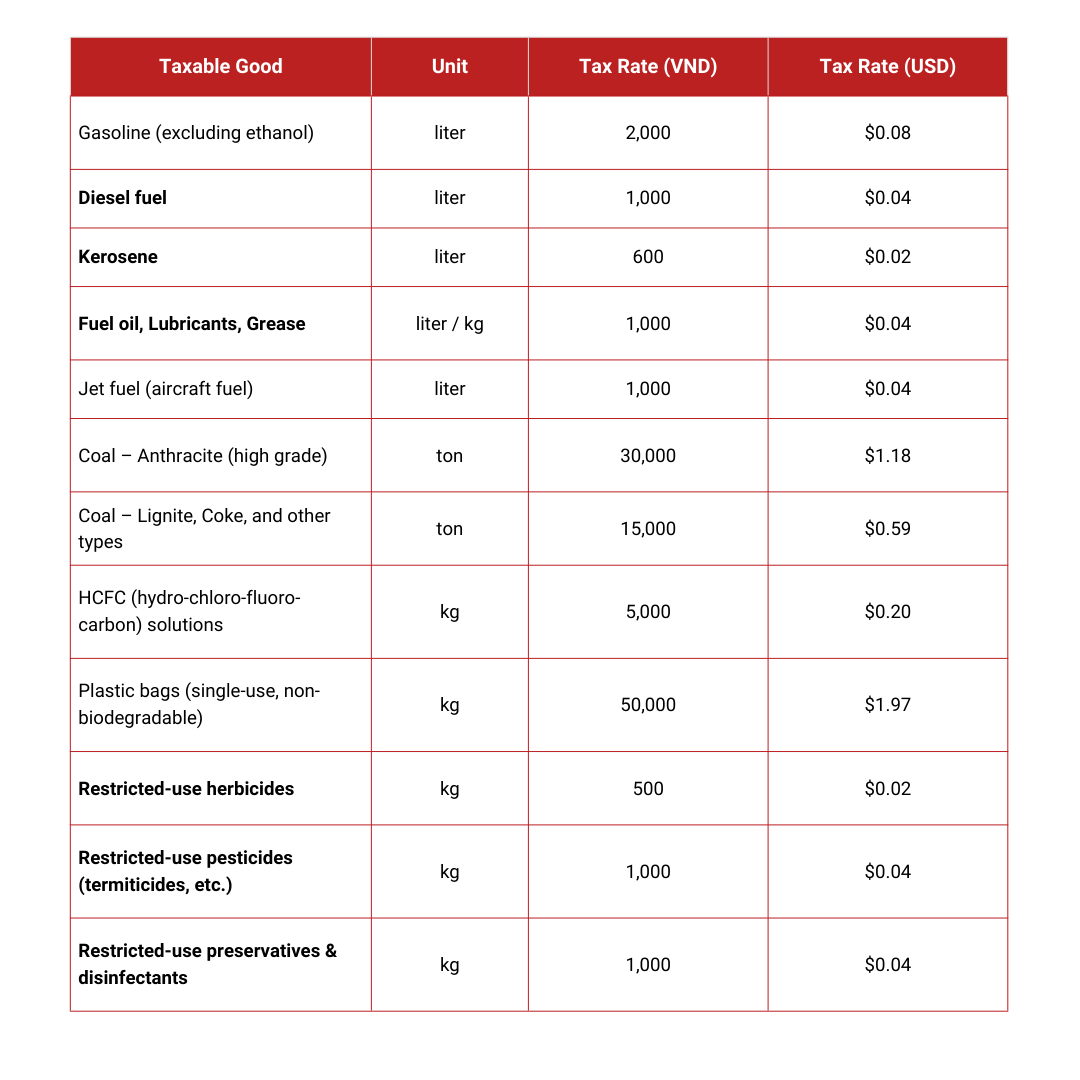
As shown above, fuel products (gasoline, diesel, etc.) and coal carry significant environmental protection tax burdens, which can affect transportation and manufacturing costs. For example, gasoline currently incurs a tax of VND 2,000 per liter (around $0.08) under this policy. Meanwhile, single-use plastic bags are taxed at VND 50,000 per kilogram (about $2 per kg), reflecting government efforts to curb plastic waste. Even certain chemicals like HCFCs (often used as refrigerants) and specific agricultural chemicals (herbicides, pesticides, etc.) are taxed due to their environmental risks. Businesses dealing with these materials need to factor in these fixed costs when pricing products or planning operations.
It’s important to note that the tax rates on some goods have been temporarily reduced by the government in recent years to support economic recovery. For instance, the rates on fuels listed above include a special reduction in effect through December 31, 2025. These reduced rates (e.g. VND 2,000 per liter for gasoline, which is half of the statutory rate of VND 4,000) are slated to revert to higher levels starting in 2026 unless further extended.
Startups and SMEs should keep track of such changes because an increase in the environmental protection tax on fuels or other inputs will directly impact operating costs. In the table, all VND figures reflect the current 2025 rates, incorporating the temporary cuts. Future adjustments by the authorities – such as ending a tax cut or introducing new taxable items – could change these numbers, so always verify the latest rates from official sources.
Who Pays the Environmental Protection Tax?
The responsibility for paying the Vietnam environmental protection tax falls primarily on businesses that produce or import the taxable goods. In practice, this means if your company manufactures any of the above-listed products domestically, or if you import them into Vietnam, you are liable for the tax. The law requires producers and importers to declare and pay the tax at the time of sale or importation, respectively.
- Domestic producers of taxable goods must calculate the tax for all goods produced and sold (or even given away) each month, and then file a tax declaration and payment on a monthly basis. For example, a plastic bag manufacturer in Vietnam needs to tally how many kilograms of taxable bags it distributed in a month and pay the corresponding environmental protection tax for that month.
- Importers of taxable goods must pay the environmental protection tax at the point of import, together with import duties and other taxes during customs clearance. Essentially, when you bring goods like fuel or chemical products into Vietnam, the tax is assessed as part of the import process and is usually paid before the goods are released from customs.
In cases where goods are imported through an intermediary or trading company (i.e., an entrusted import), the entity that entrusts the import is considered responsible for the tax. This ensures that every taxable product entering Vietnam’s market has the environmental protection tax accounted for, regardless of the import arrangement. The design of this tax follows the “polluter pays” principle – those who introduce environmentally harmful goods into circulation (producers and importers) have to bear the tax cost. However, these businesses typically pass on the cost in product pricing, meaning ultimately the consumers of the goods indirectly pay for the environmental impact.
It’s worth emphasizing that most regular businesses and consumers do not file or pay this tax directly. If you run a company that only uses these products (for example, you purchase fuel for your vehicles or buy plastic packaging from suppliers), the tax is embedded in the price you pay to your supplier. Only the businesses at the start of the supply chain (the producers or importers) handle the administration of the Vietnam environmental protection tax. That said, the tax can still affect your bottom line indirectly, so understanding it can help in managing costs (e.g. choosing more eco-friendly inputs that might not carry such taxes).
Download: Practical Guide to Corporate Tax & Compliance Work in Vietnam
Calculation of Environmental Protection Tax
Calculating the amount of environmental protection tax due is relatively straightforward because it’s based on a fixed rate per unit of goods. The basic formula is:

Each type of taxable product has a specific tax rate per unit (as shown in the table above), so to compute the tax, a business simply multiplies the volume of goods (number of units) by the applicable rate. For example, if an importer brings in 10,000 liters of diesel fuel, and the tax rate for diesel is VND 1,000 per liter, the environmental protection tax would be 10,000 × 1,000 = 10,000,000 VND for that shipment. Similarly, a plastics manufacturing company producing 500 kg of non-biodegradable plastic bags in a month would calculate that month’s tax as 500 × 50,000 = 25,000,000 VND.
While the formula is simple, businesses must be meticulous in tracking quantities of taxable goods. For domestic producers, this means keeping accurate records of production, sales, and even internal use of the goods. Note that if taxable goods are used internally, given away as samples, or used for promotions, they still count as taxable usage under the law. In other words, anytime you take products out of inventory for any purpose (sale, internal consumption, or free distribution), you need to account for the environmental protection tax on those goods. Failing to include certain quantities (whether intentionally or by accident) could lead to underpayment and penalties.
For imported goods, accurate customs declarations are key. The customs authorities will assess the environmental protection tax based on the quantity declared on the import documents. Double taxation is avoided – once the tax is paid at import or production, the goods can be sold down the line without additional environmental tax. For instance, if a wholesaler buys fuel from an importer, the importer has already paid the tax at customs, so the wholesaler doesn’t pay the tax again. However, if that wholesaler then exports the fuel out of Vietnam, no environmental protection tax applies to the export (since the tax is meant to address environmental harm within Vietnam only).
Filing and Paying the Vietnam Environmental Protection Tax
Declaring and paying the Vietnam environmental protection tax is a routine part of tax compliance for producers and importers of the taxable goods. The process and frequency of filing depend on whether the goods are produced domestically or imported:
- For domestically produced taxable goods: Businesses must file an environmental protection tax declaration monthly, together with other periodic tax filings. The tax period is typically one calendar month, and the declaration and payment are usually due by the 20th day of the following month (in line with Vietnam’s general tax administration timeline). For example, for goods produced in January, the tax return should be filed and tax paid by February 20. The declaration should detail the quantity of each taxable good produced and sold (or used) in that month and the corresponding tax amount. The monthly filing requirement means companies need to incorporate the environmental protection tax into their regular accounting cycle.
- For imported goods: The environmental protection tax on imports is paid at the same time as import duties and VAT during the customs clearance process. In practice, when you (or your shipping agent) file the customs declaration for an incoming shipment that includes taxable goods, the customs system will calculate the environmental protection tax due based on the quantities. You must pay this tax (along with any import duty) before the goods are cleared from customs. There is no separate monthly filing for imports; each import shipment’s tax is handled per occurrence at the port of entry. If you use an import-export service or freight forwarder, they will usually handle this on your behalf, but the cost is passed on to your company.
Payment methods: The payment of Vietnam environmental protection tax is typically made via non-cash methods. Businesses can pay through bank transfer into the designated State Treasury account or through authorized collecting banks. For monthly domestic tax declarations, many companies use the electronic tax payment system provided by the tax authorities. Vietnam has been improving its e-tax infrastructure, allowing online filing and payments, which simplifies compliance for businesses with high volumes of transactions. According to guidance, taxpayers may submit their environmental protection tax declarations in person, by mail, or electronically if available. In practice, most medium and large businesses now use electronic filing (via the General Department of Taxation’s e-tax portal), which is both convenient and provides a record of submission.
It’s crucial to pay on time. If the environmental protection tax is not paid by the deadline, late payment interest will accrue as per the Tax Administration Law (usually 0.03% per day on the overdue amount, or the prevailing rate set by law). Consistent late filing or payment can also trigger penalties or audits. Startups and SMEs should set up reminders in their accounting calendars for these tax obligations to avoid incurring unnecessary fines. Note that the tax authorities and customs offices are generally available to provide guidance on the procedures – it’s advisable to consult with the tax office or a professional tax advisor if you are filing for the first time or have an unusual situation.
Record-keeping: As with all taxes, maintaining thorough documentation is part of compliance. Retain copies of monthly declarations, tax payment receipts, and customs documents for imports. These records will be important if there’s ever a question or audit about whether the correct environmental protection tax was paid. Good record-keeping also facilitates any potential tax refund claims, which we discuss next.
Read More: An Essential Guide of Taxation & Compliance Deadlines in Vietnam
Environmental Protection Tax Refunds
In certain scenarios, a business may be eligible for a refund of environmental protection tax already paid. Refunds are not common, but they can apply in situations where the taxed goods do not end up being used in Vietnam’s domestic market or where an exemption condition is met after the fact. Key cases include:
- Re-exported goods: If your company paid environmental protection tax on imported goods, but then you re-export those goods without using them domestically, you can apply for a refund of the tax. For example, importing fuel or raw materials that are later exported to another country could qualify, since the environmental impact in Vietnam is avoided in the end. The goods must be under customs supervision for re-export or follow the procedures for temporary import for re-export.
- Certain plastic packaging for export: Vietnam’s law exempts “plastic bags used for pre-packaged goods” from the environmental tax. In practice, manufacturers or importers of packaging materials that are used to package exported products might pay the tax upfront but can claim a refund upon proving the bags were used for exported goods. The intent is to not penalize businesses for packaging that leaves Vietnam with the exported goods. If your SME produces or imports plastic packaging and supplies it for products that are shipped overseas, look into this refund opportunity.
- Unused imports or transshipments: If taxed goods were imported but remain unused and are stored in bonded warehouses or at port, and then are re-exported or sold to a foreign entity directly, a refund can be claimed since they did not enter domestic consumption. Also, goods temporarily imported for trade fairs or exhibitions that are re-exported can have the tax refunded.
To get a refund, a business must submit a written request and supporting documentation to the tax authorities or customs office (depending on the case). Documentation typically includes proof of the original tax payment (tax receipts or customs declarations) and evidence of the goods’ re-export or exempt use (such as export customs documents, contracts, or usage statements). Accuracy and completeness are crucial – any inconsistencies in paperwork can delay or nullify the refund.
The tax authority will verify the claim and, if approved, process the refund to the taxpayer’s account. Keep in mind that refund procedures can take some time and require careful compliance with guidelines, so it’s often advisable to consult with a tax professional or customs expert when preparing a refund claim. For most startups, unless you are directly in the business of importing/exporting the taxed goods, refunds won’t be a regular concern – but it’s good to be aware that this mechanism exists.
Read More: Legal Advisory Services In Vietnam: Guide to Navigate Complexities
Recent Updates to Vietnam Environmental Protection Tax Policy
Recent developments in Vietnam’s environmental protection tax policy reflect the government’s ongoing commitment to enhancing environmental sustainability.
Extension of Reduced Fuel Tax Rates Through 2025
To support economic recovery post-COVID and control inflation, Vietnam extended its reduced environmental protection tax rates on fuels through December 31, 2025. Originally, the tax cuts on gasoline, diesel, and similar products were set to expire at the end of 2024, but the National Assembly Standing Committee prolonged them via Resolution 60/2024/UBTVQH15. Under this extension, the EPT on gasoline remains at VND 2,000 per liter (instead of the standard VND 4,000), and on diesel at VND 1,000 per liter, among other fuel rates. These reduced rates will stay in effect until the end of 2025.
Starting January 1, 2026, fuel tax rates are scheduled to revert to their higher levels as defined by an earlier resolution (579/2018). Businesses, especially those in transportation or manufacturing with heavy fuel usage, should be prepared for a potential increase in fuel costs after 2025 if no further extensions are granted. It may be wise to factor this into financial planning or invest in fuel efficiency to mitigate the impact of a future tax jump.
New Regulations on Emission Fees (Effective January 2025)
In addition to the traditional environmental protection tax on goods, Vietnam has introduced a new environmental protection fee on industrial emissions starting from January 2025. According to Decree No. 153/2024/ND-CP (effective January 5, 2025), facilities that discharge significant industrial emissions (those required to obtain an environmental permit for their air emissions) are subject to this fee. The key points of the new emission fee regulation are:
- A fixed annual fee of VND 3,000,000 (approximately $125) per facility, applied to all regulated emitters.
- A variable fee based on emission volume and type of pollutant, charged per kilogram of pollutant released. Different pollutants have different rate schedules, encouraging companies to reduce harmful emissions.
- Payment schedule: Firms with automatic emission monitoring systems will report and pay quarterly, while others will do so annually. This ensures more frequent accountability for those capable of real-time monitoring.
- Collection and administration: The fee is managed by local authorities (usually the provincial Department of Natural Resources and Environment), rather than the tax office, since it’s an environmental fee. Companies will work with these local agencies to file their emission reports and pay the fees.
This emission fee is separate from the product-based environmental protection tax, but it complements the overall policy framework. For businesses in sectors like manufacturing, power generation, or processing that have factories, this means additional compliance work – you’ll need to measure emissions, perhaps invest in monitoring equipment, and allocate budget for these fees. On the positive side, the policy incentivizes companies to adopt cleaner technologies and pollution controls. Reducing emissions not only lowers the fee you have to pay but also aligns with global environmental standards that many foreign partners and customers increasingly expect.
Vietnam’s Commitment to Net-Zero Emissions
Vietnam’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, announced at the CoP26 conference in Glasgow, marks a significant milestone in the country’s environmental policy. This ambitious goal involves a comprehensive strategy that includes promoting investments in cleaner energy technologies and reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 9% using domestic resources and by 27% with international support by 2030.
As part of this strategy, Vietnam plans to expand its wind and solar power generation capacity to between 31-38 gigawatts by 2030. The country also aims to halt deforestation by 2030 and eliminate coal power generation by 2040. These initiatives highlight Vietnam’s dedication to reducing its carbon footprint and mitigating the environmental impacts of traditional energy sources.
The Environmental Protection Tax plays a pivotal role in funding these initiatives, providing the financial resources necessary to support the country’s transition to a sustainable economy. Aligning tax policy with environmental goals helps Vietnam take significant steps toward a greener future.
Impact on Foreign Firms
Foreign firms operating in Vietnam must navigate the complexities of the environmental protection tax to ensure compliance and manage their operational costs effectively. Understanding these tax obligations is crucial for foreign businesses, as non-compliance can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions.
Compliance with Vietnam’s environmental tax regulations can be challenging due to the intricate and evolving nature of local tax laws. Foreign firms need to stay informed about any changes in tax policy and adapt their business practices accordingly. This involves regular consultation with local tax authorities and legal experts to ensure adherence to all regulatory requirements.
The impact of increased taxes on non-biodegradable materials is a particular concern for foreign firms producing such goods in Vietnam. These businesses must evaluate their production processes and consider sustainable alternatives to mitigate the financial impact of the new tax rates, which can lead to negative environmental impacts. This helps them remain competitive while contributing to Vietnam’s environmental goals.
Read More: Top 10 Challenges of Doing Business in Vietnam: Notes and Advice for Foreign Investors
How InCorp Can Help?
Vietnam is always updating its environmental tax rules, showing its dedication to a sustainable future. Businesses operating in Vietnam need to stay informed and adjust to these changes to succeed and contribute to the country’s environmental efforts.Incorp Vietnam guides businesses through these regulations. We help you understand the tax requirements, ensure correct calculations and declarations, and keep you updated on any changes. With Incorp Vietnam, you can manage your environmental tax obligations effectively and support Vietnam’s sustainability goals. Contact Incorp Vietnam to learn how we can assist with your Environmental Protection Tax compliance.

clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly
Learn the Right Setup for Business
Expansion in the Vietnam
Frequently Asked Questions
What commitment did Vietnam make regarding emissions at the CoP26 in 2021?
- Vietnam committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 at CoP26 in 2021. This ambitious target reflects the country's dedication to addressing climate change.
What types of goods are subject to Vietnam's Environmental Protection Tax?
- Vietnam's Environmental Protection Tax applies to fossil fuels, coal, HCFC solutions, plastic bags, and various restricted-use pesticides and herbicides. These goods are targeted due to their environmental impact.
What is the tax rate for gasoline in Vietnam's Environmental Protection Tax?
- The tax rate for gasoline in Vietnam's Environmental Protection Tax is USD 0.079 per liter.






