Worried about Personal Data Protection in Vietnam under the new decree? Explore InCorp Vietnam’s Personal Data Protection Services for Businesses
Overview of Vietnam’s Personal Data Protection Law
Vietnam’s PDPL (Law 91/2025/QH15) took effect on 1 January 2026. It elevates personal data protection from decree to law, covering the full data lifecycle for Vietnamese citizens and residents (even if processed abroad). Decree 356/2025 provides detailed implementation rules, replacing Decree 13/2023. Key highlights:
Roles and Responsibilities in Personal Data Processing
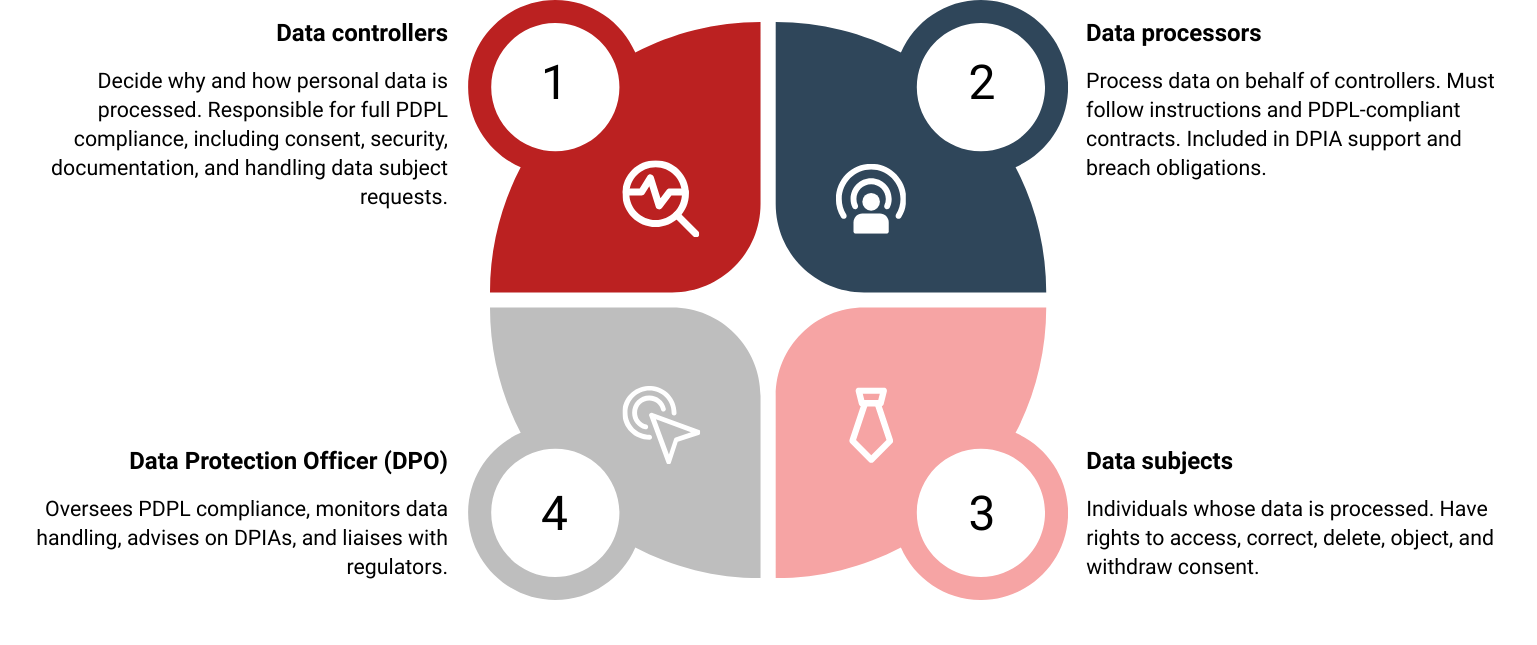
- Data Controllers: Entities that determine why and how personal data is processed. Controllers must ensure all PDPL requirements are met, from obtaining valid consent to implementing security measures. They are responsible for responding to data subject requests and retaining compliance documentation (e.g. consent logs, DPIA reports). Joint controllers (when decisions are shared) must clearly delineate roles.
- Data Processors: Entities processing data on behalf of controllers (including joint controllers). They have no independent authority; they must follow the controller’s instructions and contract terms. Under Decree 356, processors may also have to conduct DPIAs on behalf of controllers and are included in breach notifications and documentation. Contracts must explicitly bind processors to PDPL standards (see Vendor Clauses below).
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): A qualified individual or department responsible for overseeing the PDPL compliance program. The DPO’s duties include monitoring data handling, advising on DPIAs, training staff, and liaising with regulators. For smaller firms (exempt for 5 years if they meet conditions), a designated person or outsourced service may fulfill this role.
- Data Subjects: Individuals whose data is processed. They have rights to be informed, access their data, rectify inaccuracies, object to or restrict processing, delete data, and withdraw consent at any time. Controllers must facilitate these rights promptly and transparently. Respecting data subject rights is central to personal data protection and fosters trust.
Compliance Checklist & Action Plan
Phase 1 – Get Control & Structure (Foundation)
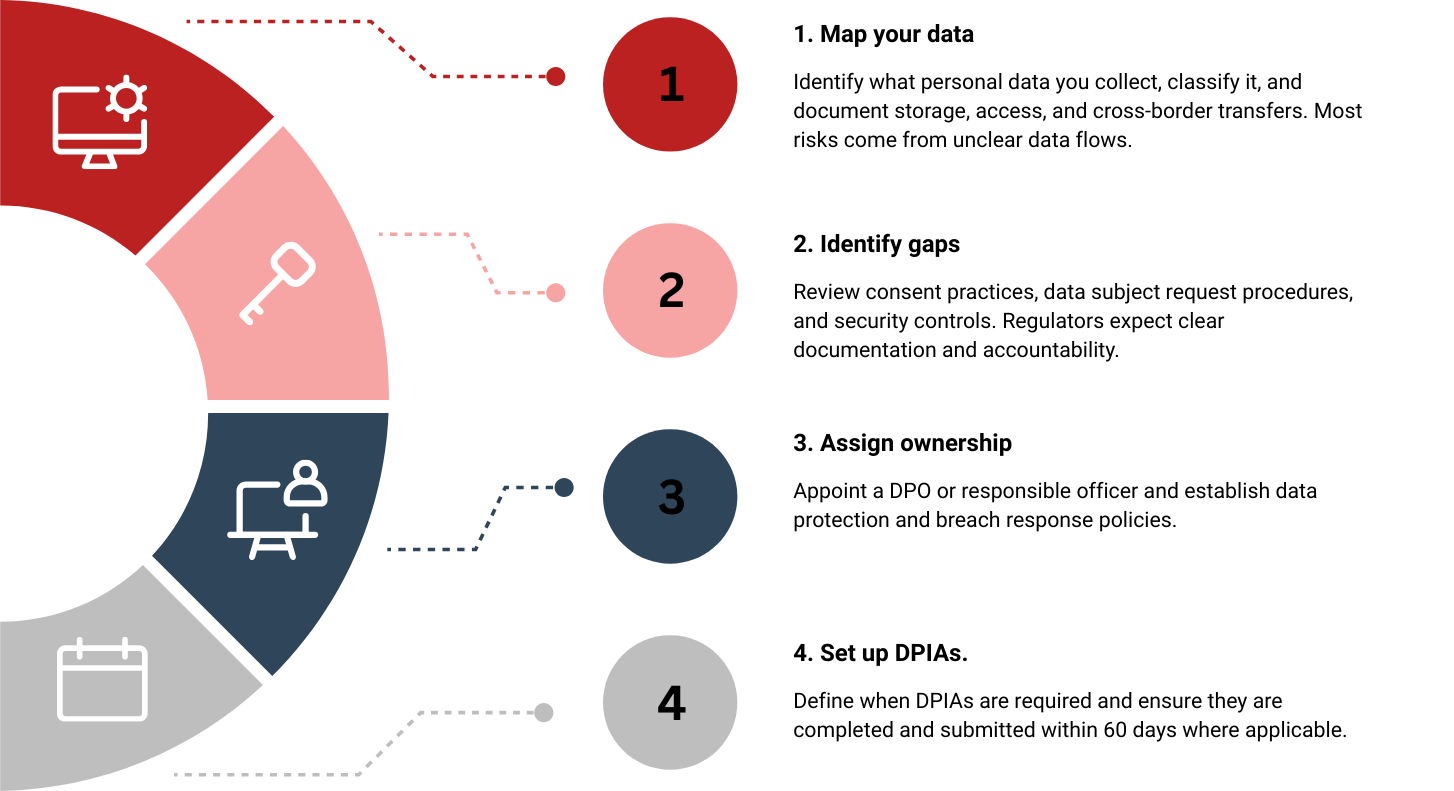
Phase 2 – Operationalize & Control Risk
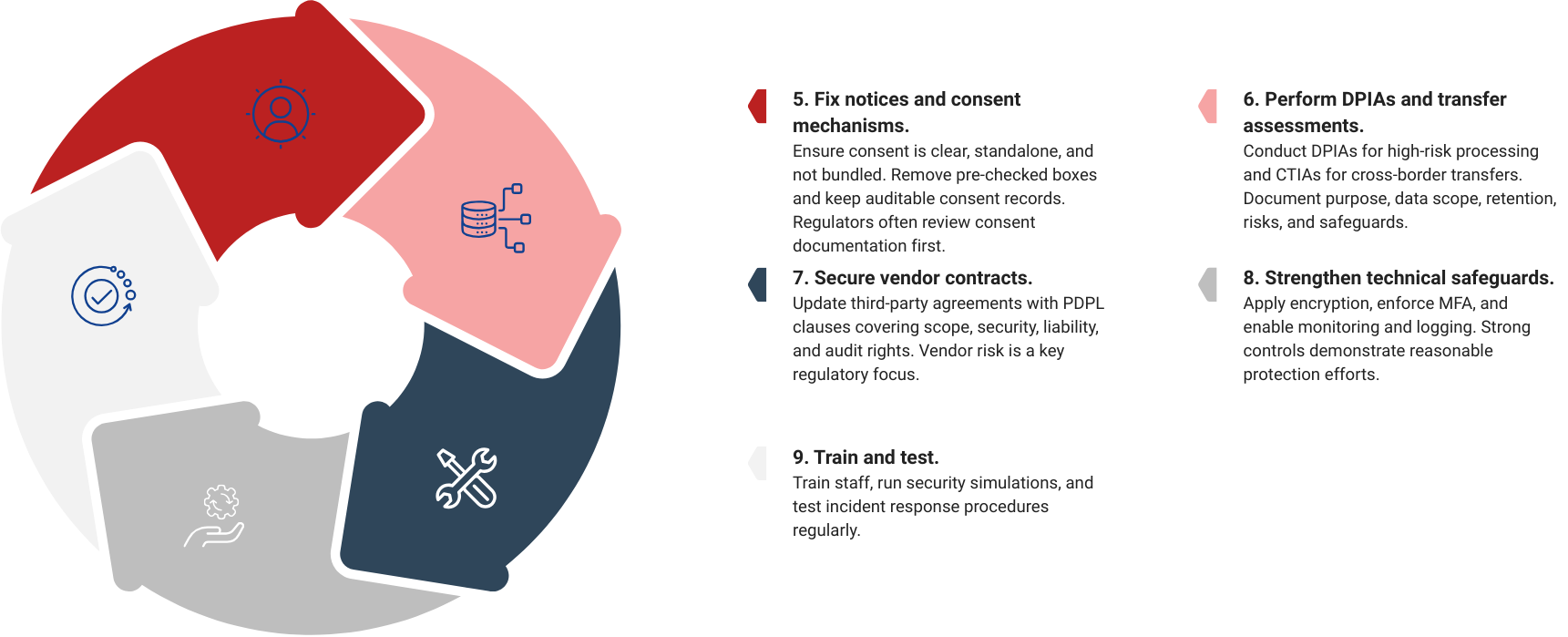
Executive Compliance Checklist (Condensed)
- Review compliance annually.
- Map and classify all personal data.
- Update privacy notices and consent forms.
- Maintain auditable consent records.
- Appoint a DPO or responsible officer.
- Complete DPIAs and CTIAs within 60 days.
- Revise vendor contracts with PDPL clauses.
- Implement encryption, MFA, DLP, and monitoring.
- Test breach response procedures.
Data Subject Rights and Response Timelines
PDPL enforces strict timelines for handling rights requests: controllers must acknowledge within 2 working days and complete requests within fixed periods. For example:
– Access/Correction: Provide data or correct errors within 10 days (can extend once by 10 days with justification).
– Deletion: Comply within 20 days (extendable once by 20 days).
– Cessation/Withdrawal: Implement within 15 days (or 20 days if involving a processor).
Organizations should establish a process to log requests, verify identity, and track deadlines. Ideally, have a standard form and SLA. Failure to meet deadlines can lead to penalties. Ensure all procedures are well-documented (for regulators) and transparent to users.
Consent Management
Under PDPL, consent methods must be verifiable and explicit. Controllers are required to:
– Use clear opt-in mechanisms (written, recorded call, SMS, email with audit trail).
– Retain records of consent (who, when, what) and be able to prove it in case of dispute.
– Avoid any default opt-ins or confusing choices. (For sensitive data, explicitly inform subjects that it is sensitive.)
– Allow easy withdrawal: the same ease as giving consent, without penalty.
A practical tip: use consent management software that logs user choices and timestamps. When obtaining consent for multiple purposes (e.g. marketing, profiling), obtain separate consents for each.
Vendor Contracts and Data Transfer Agreements
All third-party data processing or transfers must be governed by contracts meeting PDPL requirements.

For data transfers, Vietnamese law mandates a formal Data Transfer Agreement (DTA). The DTA must include all points listed in Article 7 of Decree 356: transfer purpose, data categories, retention period, legal basis, responsibilities of parties, coordination in case of breaches, etc. This DTA supplements any standard agreement (like EU Standard Contract Clauses) when transferring Vietnamese personal data abroad.
Breach Response Playbook
Personal data protection includes being prepared for incidents. The breach response process should be:
1. Detect & Classify: As soon as an anomaly or incident is detected (e.g. via SIEM alerts or user report), triage to determine if it’s a data breach affecting personal data. Classify data involved (especially if sensitive) and assess scope.
2. Containment: Immediately contain the breach (e.g. disconnect affected systems, reset credentials, patch vulnerability). Prevent further unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
3. Assessment: Convene the incident response team (including IT, legal, PR). Determine the cause, extent of data exposed, and potential impact (financial, reputational, regulatory).
4. Notification: Under PDPL, you must notify authorities if serious harm is likely. Since “serious harm” is somewhat subjective, adopt a low threshold. Even if not required, notify affected individuals promptly (so they can protect themselves). Aim to issue notifications (to regulator and/or data subjects) as soon as possible, ideally within 72 hours of discovery, mirroring GDPR best practice. Use the prescribed form via the national portal.
5. Remediation: Improve systems and processes to prevent recurrence (patch vulnerabilities, enhance monitoring, update policies).
6. Documentation: Record all steps taken, timelines, decisions, and communications. This demonstrates accountability if regulators inquire.
Breach Playbook Checklist: internal notification procedures, roles (who leads containment, who communicates), communication templates (to authorities, affected users), and log of actions. Conduct post-mortems to update the incident plan.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) Template
A practical DPIA template (also applicable as a CTIA template with added sections on transfer specifics) should contain:
- Project Overview: Description of processing (e.g. “Employee health data management”). Scope, purpose, and categories of data.
- Stakeholders: Identities of Controller(s), Processor(s), third parties and their roles.
- Data Inventory: Detailed list of personal data items used (names, contact info, ID numbers, health records, etc.), indicating which are sensitive.
- Data Flow Diagram: Visual or described flow of data between systems and parties.
- Risk Identification: Potential harms to data subjects (financial, reputational, physical safety, etc.), along with likelihood and severity.
- Existing Controls: List of current safeguards (technical and organizational) addressing each risk (e.g. encryption, access controls, personnel training).
- Residual Risk & Severity: Evaluate remaining risk after controls (e.g. “Low/Medium/High”).
- Mitigation Plan: Additional measures (e.g. stronger encryption, data minimization, policy changes) to further reduce risk.
- Outcome: Risk level summary and decision (e.g. proceed with processing, add measures, or reduce scope).
- Documentation: Keep copies of signed risk reports and evidence of implementation.
(Cross-Border DPIA additions: Identify destination countries, legal basis, adequacy status, and emergency plan if foreign law conflicts. Decree 356 exempts some cross-border cases (like employee cloud storage).)
Vendor & Contract Clause Examples
- Data Scope & Purpose: “Vendor shall process only the personal data categories (e.g., Name, ID, phone) necessary for [purpose] and in compliance with Controller’s instructions.”
- Duration & Deletion: “Upon end of contract or request, Vendor will delete/destroy personal data and all copies within [X] days.”
- Security Measures: “Vendor must implement technical safeguards equivalent to Controller’s (e.g. AES-256 encryption, role-based access). For transfers of sensitive data, the Vendor will use encryption and anonymization.”
- Compliance & Audit: “Vendor agrees to periodic audits of its data protection controls and to promptly notify Controller of any breach.”
- Data Subject Assistance: “Vendor shall assist Controller in fulfilling data subject requests and must not interfere with subjects exercising their rights.”
- Subprocessor Restrictions: “Vendor shall not sub-contract personal data without Controller’s consent and will impose the same obligations on any sub-processor.”
(These clauses reflect Decree 356 requirements like Article 7 on transfer agreements.)
How InCorp Vietnam can Help?
InCorp Vietnam helps organizations establish robust data protection frameworks, ensuring they meet legal obligations while fostering trust with clients. By partnering with InCorp Vietnam, companies can stay ahead of emerging data protection trends, ensuring compliance and maintaining a strong culture of privacy and security in the digital age.

clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly
Learn the Right Setup for Business
Expansion in the Vietnam
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key responsibilities of data controllers?
- Data controllers are responsible for determining the purposes and means of processing personal data, as well as ensuring compliance with data protection laws to protect the rights of data subjects. Their role is crucial in maintaining data privacy and security.
How does Vietnam's Personal Data Protection Decree (PDPD) align with GDPR?
- Vietnam's Personal Data Protection Decree (PDPD) aligns with GDPR by incorporating key principles of data protection, thereby enhancing safeguards for personal data for all companies operating in Vietnam. This alignment reflects a commitment to robust data privacy standards.
What are the essential technical measures for protecting personal data?
- To effectively protect personal data, implementing encryption, data loss prevention systems, robust network security measures, and stringent user authentication protocols is essential. These measures are crucial in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches.
Why are data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) important?
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) are essential for assessing risks linked to the processing of personal data and for identifying potential adverse effects. They enable organizations to implement effective measures to reduce these risks and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.






