For global manufacturing firms looking for diversity and to strengthen the resilience of their supply chains, Vietnam has emerged as a prominent target. Vietnam presents an exceptional opportunity for foreign investors due to its stable political system, dedication to sustainable growth, low inflation, high FDI inflows, young and technologically advanced population, and dynamic industrial zones. With GDP growth of 7.09% in 2024 and FDI inflow rising nearly 34.7% to US$10.98 billion in Q1 2025, Vietnam’s appeal has further strengthened.
Currently, Vietnam is home to over 400 planned industrial zones, with around 300 already operational and maintaining an impressive average occupancy rate exceeding 80%. Following provincial-level mergers effective July 1, 2025, the key units driving industrial growth now include Ho Chi Minh City (incorporating former Bình Dương and Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu), Dong Nai (expanded with Bình Phước), Bac Ninh, Hải Phòng (expanded with Hải Dương), and Long An.
National Performance in 2024 & Q1 2025
In Q1 2025, the northern region maintained occupancy at around 80% , absorbing approximately 200 hectares of industrial land, reflecting sustained demand in electronics and high-tech manufacturing . The southern region continued at an 89% occupancy rate , upheld by robust activity in Ho Chi Minh City, Long An, and former Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu.
Looking ahead, Vietnam is expected to introduce some 15,200 ha of new industrial land supply and over 6 million m² of warehouse and factory space between 2024 and 2027, positioning the market for continued expansion.
Read More: Doing Business in Vietnam as a Foreigner: What, Where, Why, How?
Rental prices in northern industrial zones continued to narrow the gap with those in the south, driven by rising demand in key markets such as Hai Duong and Hai Phong (Hai Duong was merged to Hai Phong City now). By Q1 2025, the average industrial land rent in the north surged to US$139 per m² for the remaining lease term, marking nearly a 4% YoY increase. In the south, the average asking rent stood at US$170 per m², up modestly quarter-on-quarter, driven by tight land availability in key southern hubs
Investing in Vietnam? Check Out InCorp’s Incorporation Services in Vietnam
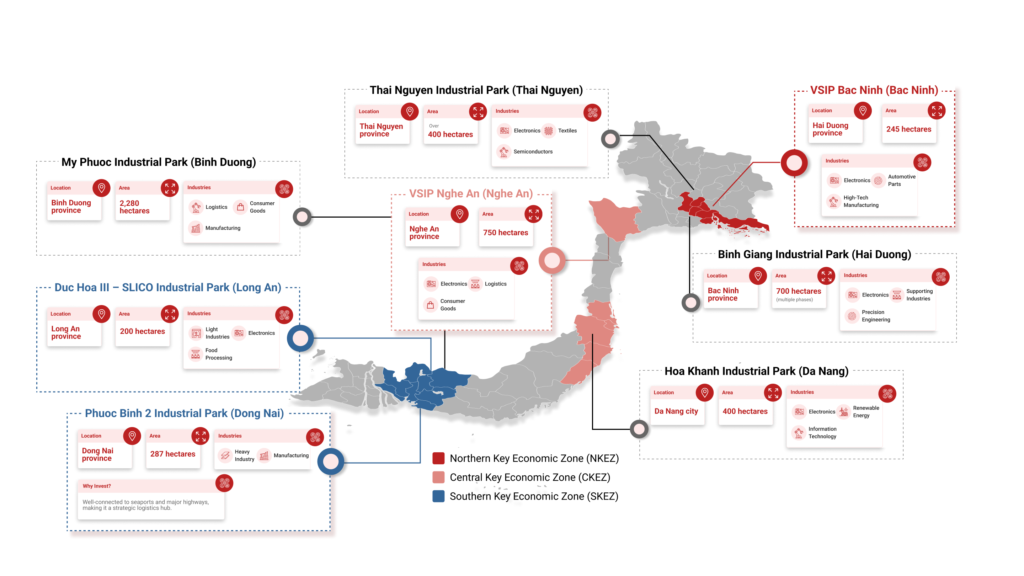
Northern Industrial Hubs
City of Hanoi
Hanoi is the capital of Vietnam and is situated in northern Vietnam on the western bank of the Red River, about 85 miles (140 km) inland from the South China Sea. The City has a population density considerably higher in the urban area, approaching 20,100 per square kilometer.
Hanoi has been developing several critical industries selectively during 2021-2015, focusing on the sectors and products using cutting-edge technologies and having high added value. The development of high-tech businesses with significant export potentials, such as digital control, automation, robotics, nano, plasma, laser, and biotechnology, is gradually changing the City’s industrial sector.
Other manufacturing sectors, such as motor vehicles, shipbuilding, food processing, steel, petrochemicals, and software, have been identified as crucial.
Hanoi has been developing industrial parks for the 2021-2025 period. Hanoi has 70 operational industrial clusters and grasslands in 17 districts and towns, covering 1,868 hectares and contributing significantly to economic development and social welfare.
One of the most well-known industrial parks is Hoa Lac Hi-tech Park, which services businesses in the commerce and software development industries. It is the first and largest hi-tech park in Vietnam, with a total area of 1586 hectares in Hanoi’s Capital. The park consists of the following main function industrial zones:
- Software development zone
- Training and research zone
- High-tech industrial zone
- Residential zone
- Service zone
Read More: Hanoi Business Incorporation Guide: Opportunities, Requirements, and How-To Steps
Haiphong
Hai Phong is one of the largest and most important seaports in Northern Vietnam. It is also one of the most modern seaports in Southeast Asia, with advanced navigation and networking facilities. Hai Phong Port handles large cargo and passengers and is an essential gateway for Vietnam’s trade with other countries. The port is located on the coast of the Gulf of Tonkin, which is one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world.
Industry is critical in Haiphong, including food processing, light, and heavy industries. Some major industries in Haiphong are shipbuilding, textiles, cement, paper, steel, and chemicals. Haiphong has traded goods with more than 40 countries and territories worldwide. Haiphong is also home to many factories and industrial parks. It is striving to become one of the largest commercial centers in the country.
As of July 1, 2025, the newly consolidated Hải Phòng province (now including former Hải Dương) continues to oversee its 12 major industrial parks within Hải An, An Dương, and Thủy Nguyên districts, with improved regional connectivity and expanded labor markets
Most of the large industrial parks in Hai Phong are in three districts: Hai An, An Duong, and Thuy Nguyen. These districts share the same borders and have good access to the airport, the seaports, and main roads like National Highway 5A.
Central Industrial Hubs
Danang
Danang is located in the South Central Coast geography zone of Vietnam. The terrain of Danang includes mainlands and islands. Danang is the largest city in central Vietnam and one of the country’s most important ports. The mountains surround the City to the west, and the South China Sea is to the east.
Danang’s key industries include machinery, electronics, chemicals, and shipbuilding. Shipbuilding is an attractive industry, with the South China Sea tensions boosting demand for naval and coast guard ships.
Danang City has six concentrated industrial parks, including Hoa Khanh, Da Nang, Lien Chieu, expanded Hoa Khanh, Hoa Cam, and Danang Fisheries Services, with a scale of 1,066.52 ha. Lien Chieu Industrial Park is one of them, located in Lien Chieu district, Danang city. The park has an area of 1,200 hectares and is expected to attract investment in electronics, mechanics, and high-tech industries.
Quang Nam – Danang economic zone
The Quang Nam– Danang economic zone is one of the key industrial zones in Central Vietnam. It comprises Thua Thien Hue, Danang, Quang Nam, Quang Ngai and Binh Dinh provinces. This region plays a significant role in the socioeconomic development strategy and ensures the security and defense of the Central Coast and Central Highlands.
The primary industries in the Quang Nam: Da Nang economic zone are food processing, textiles, building materials, and paper and forest products. However, oil and gas, shipbuilding, logistics, and other high-tech industries will increase in the next few years.
Several industrial parks are in the Quang Nam – Da Nang economic zone. Some of the prominent ones include:
- Dien Nam – Dien Ngoc Industrial Park: Located in the Dien Ban district, Quang Nam province’s Dien Nam and Dien Ngoc communes. The park has a 418-acre surface area.
- Hoa Cam Industrial Park: Located in Cam Le District, Danang City. The park covers an area of 261 hectares.
- Lien Chieu Industrial Park: Lien Chiểu Industrial Park now operates under the unified administration of the new Da Nang province (merging Quang Nam) to streamline land allocation and infrastructure development across the expanded zone.
Read More: Competitive Advantages of Doing Business for Foreigners in Quang Nam Province, Vietnam
Southern Industrial Hubs
Ho Chi Minh City
Ho Chi Minh is the largest city in Vietnam. The City is located on the Saigon River and is Vietnam’s principal port and largest City, with an estimated population of over eight million. The City covers about 2,061 km2.
Ho Chi Minh City is home to several key industries and sectors. Some of the prominent ones include:
- Textile and garment industry: The city is one of the largest textile and garment manufacturing centers in Vietnam
- Electronics industry: The city has a growing electronics industry with several multinational companies having their manufacturing plants in the city
- Food processing industry: The city has a well-developed food processing industry with several large companies having their manufacturing plants in the city
- Chemical industry: The city has a well-developed chemical industry with several large companies having their manufacturing plants in the city.
As of July 1, 2025, Ho Chi Minh City has expanded to include former Bình Dương and Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu provinces, creating a mega-urban zone with over 14 million residents and streamlining industrial governance.
Some of the notable industrial parks in Ho Chi Minh City include:
- Hiep Phuoc Industrial Park: Located in Nha Be District, Ho Chi Minh City. With a total area of 1,686 hectares, Hiep Phuoc is the largest industrial park in the city
- Saigon Hi-Tech Park: Located 15 km from downtown Ho Chi Minh City, opposite Thu Duc University Village. The park covers an area of 326 ha (95% utilized) and is currently being expanded to 913 ha.
- Tan Tao Industrial Park: Located in Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City. The park covers an area of 400 hectares and is home to over 200 companies.
Dong Nai
Southeast Vietnam’s Dong Nai province may be near Ho Chi Minh City. It is part of Vietnam’s southern critical economic region and has attracted investments in electronic component manufacturing, textile and garment production, and tech-intensive industrial goods manufacturing.
Dong Nai has attracted investments in the production of textiles and apparel, electronic component manufacturing, and technologically complex industrial items.
Some of the major industrial parks in Dong Nai include:
- Amata Industrial Park: Located in Bien Hoa City, Dong Nai Province. The park covers an area of 700 hectares and is home to over 200 companies
- Long Duc Industrial Park: Located in Long Thanh District, Dong Nai Province. The park covers an area of 400 hectares and is home to over 100 companies
- Song May Industrial Park: Located in Trang Bom District, Dong Nai Province. The park covers an area of 300 hectares and is home to over 100 companies
Following its merger with Bình Phước effective July 1, 2025, the expanded Dong Nai province is poised to leverage its enlarged territory and population for enhanced industrial and agricultural development.
Can Tho
Can Tho is the largest city in the Mekong Delta, located on the western bank of the Hau River, and is the economic and cultural center of the region. It is also the gateway to the floating markets, the biggest tourist attraction in the area.
Can Tho is known for its agricultural products such as rice, fruit, and fish. The City is also home to many industrial parks and factories that produce textiles, garments, footwear, and other consumer goods.
Several industrial parks in Can Tho are prominent. Two of them are the Tra Noc 1 and 2 industrial parks. These parks have been transformed into eco-industrial park models, saving 19,000 tons of oil, 30,000 tons of coal, 600,000 m3 of water, and 130,000 tons of CO2.
Why have Vietnam’s Industrial Hubs become attractive to foreign manufacturers?
Vietnam Emerges as a Top Destination for Foreign Manufacturing Companies
In recent years, Vietnam has emerged as a top destination for foreign manufacturing companies seeking to diversify and increase the resiliency of their supply chains. With a stable political system, commitment to sustainable growth, relatively low inflation, strong FDI inflows, a youthful and digital population, and a robust manufacturing sector, Vietnam offers an extraordinary opportunity for international investors. Vietnam achieved GDP growth of 7.09% in 2024 and registered FDI inflows of US$10.98 billion in Q1 2025, up 34.7% YoY . Following provincial mergers effective July 1, 2025, key manufacturing hubs now include Ho Chi Minh City (incorporating Bình Dương and Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu), Dong Nai (expanded with Bình Phước), Da Nang (merging Quang Nam), and Hải Phòng (merging Hải Dương)
Strategic Location and Advantages in Shipping
Vietnam has emerged as a desirable destination because of its strategic position and advantages in shipping as international corporations look to reduce their dependence on China and take advantage of regional growth potential. The 1,450 km East–West Economic Corridor now cuts transit times between Bangkok and Yangon from two to three weeks to just three days, offering seamless overland access from the Indian Ocean to the South China Sea and facilitating faster, lower-cost logistics for export-oriented manufacturers
Competitive Labor Costs
One of the key advantages that make Vietnam an attractive destination for foreign manufacturing companies is its competitive labor costs. Compared to other countries in the region like China or Thailand where labor costs are rising fast due to economic development or demographic shifts leading towards aging populations; According to a Boston Consulting Group report, Vietnam’s average hourly manufacturing wage of US$3 in 2020 was roughly 54% lower than China’s US$6.50, providing a significant cost advantage for labor-intensive industries.
Tax Incentives, Cost Advantages, and Efficient Taxation Policies
Vietnam’s manufacturing sector continues to attract foreign investment thanks to its competitive tax incentives, cost-efficiency, and favorable taxation policies specifically designed for the industry. These advantages make Vietnam an increasingly compelling choice for manufacturers looking to expand in Asia in 2025.
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT):
- 20% CIT for processing aquatic and agricultural products.
- 10% CIT for up to 15 years in high-tech sectors like renewable energy, scientific research, software development, and environmental protection.
- 10% CIT for industries focused on education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
- Import Duty Exemptions: Machinery, equipment, and raw materials not locally produced are exempt from import duties, helping to reduce operating costs.
- Labor Cost Advantage: Vietnam’s labor costs are 40-50% lower than China’s, offering a significant advantage in regional cost efficiency.
- VAT Incentives:
- 0% VAT for exported goods, non-tariff areas, and export processing enterprises.
- 5% VAT for essential goods like foodstuffs, medical products, and agriculture.
- Standard 10% VAT for other manufacturing activities.
These efficient taxation policies and cost advantages, coupled with the country’s efforts to foster a business-friendly environment, strengthen Vietnam’s position as a competitive manufacturing hub in the region.
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
Vietnam is now party to 18 active FTAs — with two more under negotiation — providing preferential market access, reduced tariffs, and smoother trade flows with major partners such as the EU, Japan, and South Korea. These FTAs provide foreign businesses with preferential access to key global markets, reducing tariffs and facilitating smoother trade with major economies like the EU, Japan, and South Korea. This trade-friendly environment enhances Vietnam’s competitiveness, positioning it as a top choice for foreign investors seeking to capitalize on the country’s growing industrial sector.
In addition to the advantages provided by FTAs, Vietnam offers appealing tax incentives, such as preferential corporate income tax rates, import duty exemptions, and VAT incentives for manufacturers. The country’s labor costs are also 40-50% lower than China’s, providing a significant cost advantage. Together, these factors create a compelling business environment for foreign manufacturers, enabling them to reduce operational expenses, access global markets, and benefit from a skilled, affordable workforce.
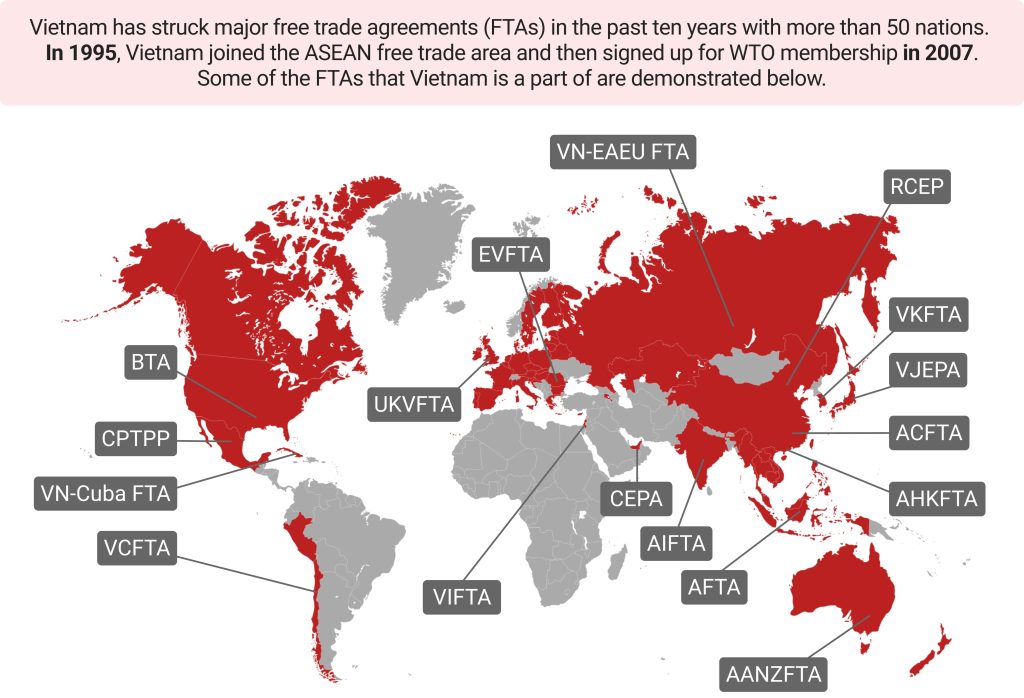
Read More: The Definitive Guide to Vietnam’s 16 Active Free Trade Agreements – FTAs
2025 Legal Updates in the Manufacturing Industry
Vietnam’s manufacturing industry has seen several recent legal updates aimed at improving the regulatory environment and aligning with international standards. These changes cover areas such as investment procedures, environmental regulations, labor laws, and tax policies. The updates are designed to enhance transparency, simplify administrative processes, and create a more favorable business climate for both local and foreign investors.
- Environmental Protection Law: According to the Decree No.153/2024/ND-CP, which came into effect on January 5th, 2025, Vietnam issued an environmental protection fee on air emissions from industrial and business facilities, advancing air pollution control policies.
- The Investment Law: According to Law No.57/2024/QH15, which came into effect on January 15th, 2025, the special investment procedures cut project implementation by 260 days by shifting from “pre-approval” to “post-check,” streamlining construction, environmental, and fire safety processes.
- Global Minimum Tax: Applicable to foreign-invested manufacturers with consolidated revenues of EUR 750 million or more in two of the last four years, requiring additional CIT to comply with global standards
Looking to navigate Vietnam’s evolving industrial regulations? Check our Tax and Legal Advisory Services
Conclusion
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Vietnam’s manufacturing industry has seen a significant uptick in foreign investment, driven by its strategic location, competitive labor costs, efficient taxation policies, and a growing network of trade agreements with key global partners. The government’s continued focus on attracting high-tech industries through incentives and FDI support policies further enhances the country’s appeal. As Vietnam positions itself as a digitally-driven, technology-ready economy, the prospects for its manufacturing sector remain highly promising. More investors are looking to expand into Vietnam, recognizing it as a stable, future-focused destination for production.
For those considering investment in Vietnam’s manufacturing sector, partnering with a trusted advisor like InCorp can be instrumental to success. Our expertise in site selection, particularly based on industry clusters, ensures that businesses find the optimal location for their operations. We assist in partnering with local suppliers and logistics providers to streamline supply chains and reduce costs. By leveraging key trade agreements like CPTPP, EVFTA, and RCEP, companies can take advantage of significant tariff benefits. Additionally, InCorp supports workforce training and localization to ensure long-term operational success and stability in Vietnam’s evolving business landscape.

clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly
Learn the Right Setup for Business
Expansion in the Vietnam
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Industries In Vietnam
- Vietnam's main industries include manufacturing (particularly electronics, textiles, and garments), agriculture (such as rice, coffee, and seafood), and tourism. The country also has a growing technology and service sector.
What Does Vietnam Manufacture
- Vietnam manufactures electronics, textiles, garments, footwear, furniture, and machinery. It is also a major producer of smartphones and consumer electronics, particularly for global brands.
What Is Industrial Zone
- An industrial zone is a designated area within a city or region allocated for manufacturing, production, and other industrial activities. It is typically equipped with infrastructure to support factories, warehouses, and related businesses.
What Is The Biggest Industry In Vietnam
- The manufacturing and processing industry is the largest in Vietnam, contributing significantly to the country's GDP. Key sectors include electronics, textiles, and footwear.






