Foreign nationals who want to visit Vietnam usually need a visa, unless they come from a country exempt from the visa requirement. There are three main ways to apply for a visa. The government offers options like a Visa on Arrival and an e-Visa for some nationalities.
Alternatively, those who are not eligible for an e-Visa, or prefer to have their visa stamped before arrival can apply at a Vietnamese Embassy in their home country. Under Immigration Laws, all international visitors must have a passport (or a valid equivalent) and an entry visa issued by the country’s competent authorities. However, visitors may be exempt from this requirement if they qualify for an exemption Vietnam visa.
This article offers a comprehensive overview of the country’s visa policy, including the application process, the different types of visas available, and the requirements for obtaining them.
Need support for a Vietnam Visa? Check out InCorp Vietnam’s Immigration Services
What is a Visa?
A visa is an official document that permits entry into a foreign country and is typically stamped or glued into the traveller’s passport. In Vietnam, visas can be issued by the competent authorities.
The E-visa, which can be obtained through an online system managed by the Vietnamese Immigration Department, allows for stays of up to 90 days and can be either single or multiple entry. Applicants can apply directly or through designated agencies and must pay a fee via an electronic payment gateway, which is non-refundable if the application is denied.
In the table below, we have listed the important visas in Vietnam and their respective definitions.
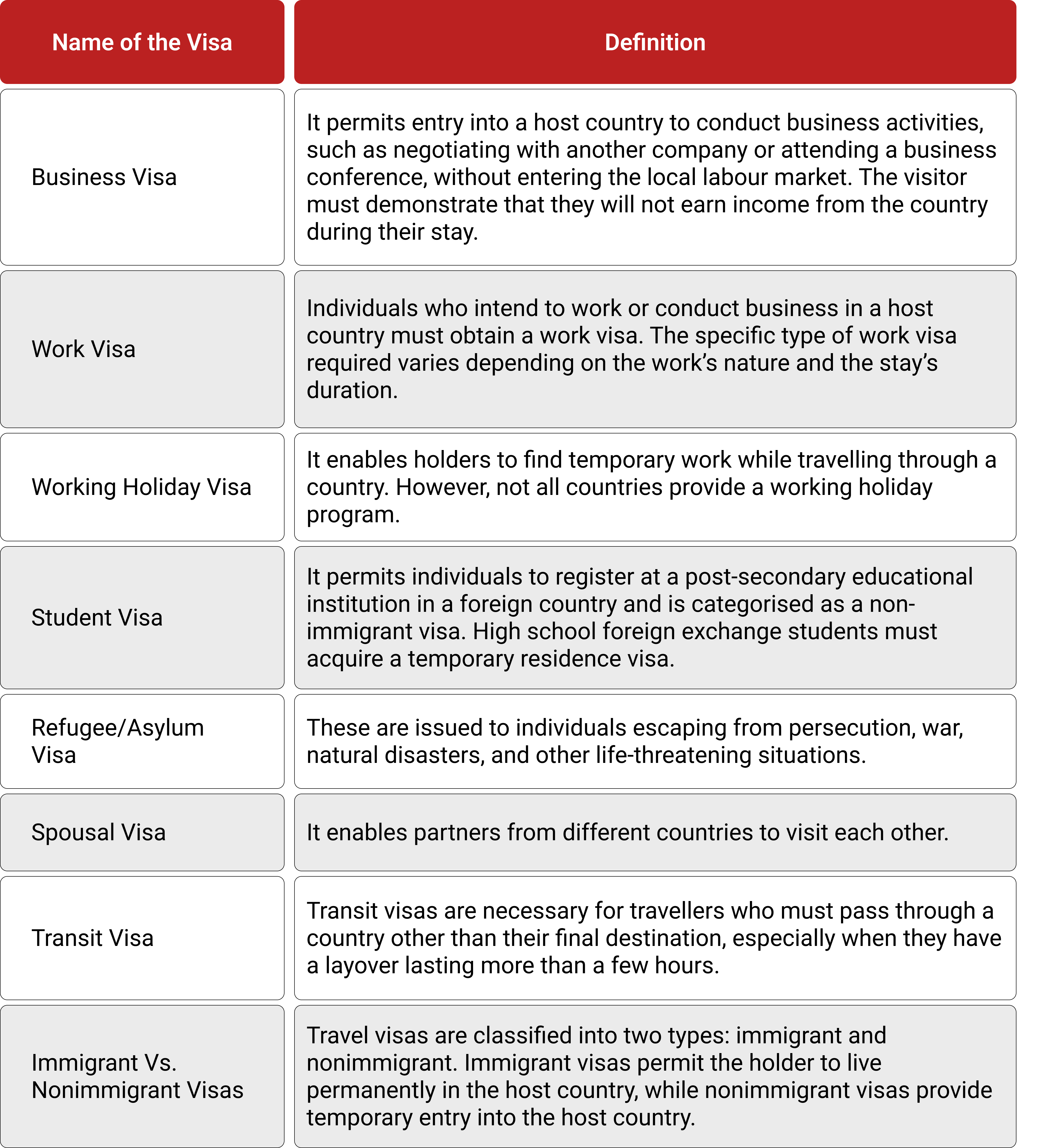
Some Types of Vietnam Visa for Foreigners
Under the new immigration laws implemented on July 1, 2020 (Law No. 51/2019/QH14), Vietnam has categorized visas into roughly 21 primary types based on visitation purposes. These are tabulated below:
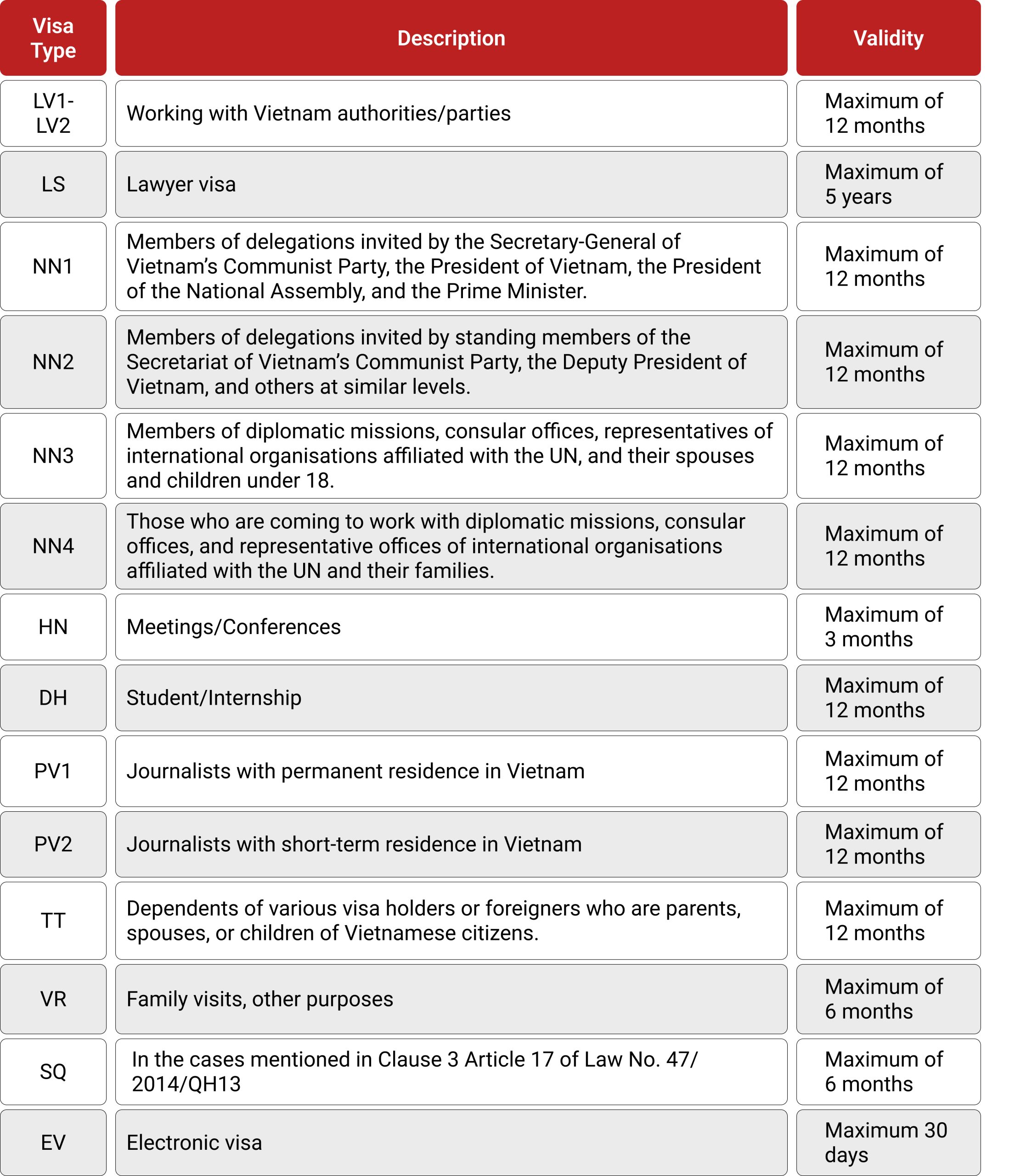
In addition, Vietnam offers the following six most popular visa types:
1. Tourist Visa
The tourist visa is specifically for those travelling to Vietnam solely for tourism purposes. This visa type prohibits any business activities within the country. It is available in the following durations and entry options:
- 30-day single entry
- 30-day multiple entry
- 90-day single entry
- 90-day multiple entry
Tourists can obtain their visas through two primary methods:
- Visa on Arrival (VOA): Suitable for air travellers who require a visa promptly.
- E-visa: This option is available for a one-month single entry and is restricted to nationals from 80 countries.
Read Related: Vietnam Travel Guide: Essential Travel Tips, Visa Requirements and Transportation Options
2. Business Visa
The business visa is ideal for those engaging in business-related activities in Vietnam without local employment. It is categorised into two types:
- DN1 visa: Issued to those working with businesses and organisations legally recognised in Vietnam.
- DN2 visa: This visa is for those offering services, establishing a commercial presence, or conducting activities under international treaties Vietnam is a member of.
The business visa is available as follows:
- 30-day single entry
- 30-day multiple entry
- 90-day single entry
- 90-day multiple entry
Methods to obtain a business visa include:
- Visa on Arrival (VOA): Highly recommended for its convenience.
- E-visa
3. Student Visa
A student visa is granted to individuals attending university courses in Vietnam. Typically, this visa is arranged after the student arrives in Vietnam. Initially, students may enter Vietnam on a tourist visa and then switch their visa status at the Immigration Office after enrolling in their course. Visa facilitation through an agency is often the most straightforward method.
4. Working Visa
This visa is for foreigners employed in Vietnam (e.g., teaching). The working visa is divided into:
- LD1: For those eligible for a work permit exemption as per international treaties.
- LD2: A work permit is required to be employed in Vietnam.
A working visa is valid for up to two years and can be extended for two more years through an LD temporary residence card.
To apply, the employer in Vietnam must secure an LD visa approval letter from the Vietnam Immigration Department. The visa can then be stamped upon arrival or at a Vietnam mission abroad, depending on the approval letter.
Read Related: Work Permit in Vietnam: Requirements, Procedures, and Agency Services for Your Vietnam Work Visa
5. Investor Visa
Investor visas are issued based on the amount of capital investment:
- DT1: For contributions of at least VND 100 billion or investments in incentivized business fields and areas, valid for up to 5 years.
- DT2: For investments of VND 50 billion to under VND 100 billion, valid for up to 5 years.
- DT3: For investments of VND 3 billion to under VND 50 billion, valid for up to 3 years.
- DT4: For investments under VND 3 billion, valid for up to 12 months.
Read More: Expanding in Vietnam by Using an Investor Visa for Foreigners
6. Diplomatic Visa
Diplomatic visas are provided to:
- Members of delegations invited by Vietnamese government officials.
- Consulate personnel and their visitors for short stays.
Diplomatic visas are typically free of charge unless otherwise stipulated by an agreement between Vietnam and the applicant’s home country. They require an official letter from the government or consulate of the applicant’s home country for application and it can be valid for up to 12 months.
Requirements and Documents for Applying for a Visa to Enter Vietnam
When you apply for a visa, you must have several documents to support your application.
They include the following:
- Passport: It must be valid for at least 6 months after your arrival date in Vietnam and contain at least two blank pages for immigration stamps. Temporary passports may not be accepted.
- Visa Approval Letter: Necessary for obtaining a business visa in Vietnam
- Photo: Two recent passport-sized photos (4×6 cm) are required, taken without glasses.
- Visa Application Form: The Immigration Entry and Exit Application Form is needed for a Vietnam visa on arrival.
- Vietnam Visa Fees
Below are some of the additional information that you must be aware of
- Travellers transiting through a Vietnam airport should verify visa requirements with their airlines.
- Travellers visiting Phu Quoc Island directly by boat or aeroplane from a foreign country and staying for less than 30 days do not need a visa.
- If you are eligible for visa-free entry into Vietnam, ensure your passport is valid for at least six months from your entry date.
- The visa approval letter is only valid for airport entries. Travellers entering Vietnam by land or cruise should apply for a visa through their local embassy.
How to Apply for a Vietnam Visa?
You have three options for submitting a Vietnam visa application:
- In-person, at a Vietnam Embassy or Consulate abroad.
- Online, if you are from one of the eligible countries.
- Upon arrival, you will receive an approval letter online before travelling.
Apply for a Vietnam Visa at an Embassy or Consulate
You can apply for your visa at any Vietnamese Embassy or Consulate abroad.
- Contact the Embassy or Consulate to schedule an appointment or to inquire about any specific requirements.
- Gather all necessary documents required for your Vietnam Visa.
- Submit these documents and pay the required Vietnam visa fee.
- Wait for the visa to be processed.
- Pick up your passport and receive information about the visa decision.
- If your application is successful, the visa will be stamped into your passport, allowing you entry into Vietnam.
Points to be Remembered
- You can submit your documents by mail depending on the country you are applying to.
- Depending on the purpose of your visit and the specific Embassy or Consulate, you might also need to provide a Letter of Approval from Vietnam’s Immigration Department.
Apply for a Vietnam Visa Online (Vietnam e-Visa)
You can apply for a visa online if you are from a country eligible for the e-Visa. To obtain a Vietnam visa online, you must:
- Initiate an online application via the Vietnam Immigration Portal.
- Upload a scanned copy of your passport and a passport-size photo of yourself.
- Fill out all necessary details on the online application form.
- Pay the Vietnam e-Visa fee (US$25).
- Wait for the visa processing, which can take up to three working days.
- Visit this website to check the status of your application.
- If your e-visa is approved, download the PDF file and print two copies.
Points to be Remembered
- The Vietnam e-Visa allows you to enter only through specific points of entry.
- It is valid for a single-entry
- It allows up to 30 days from your intended entry date into Vietnam.
Apply for a Vietnam Visa On Arrival
If you plan to enter Vietnam through one of the country’s international airports listed below, you may opt for a visa On Arrival:
- Tan Son Nhat in Ho Chi Minh City
- Noi Bai International Airport in Hanoi
- Danang Airport in Da Nang
- Cat Bi Airport in Hai Phong
- Cam Ranh Airport in Nha Trang
Before applying for a Visa On Arrival, you must obtain an Approval Letter from the Vietnamese Immigration Department. This can be arranged through a travel agency or a visa application service that the Vietnam Immigration Department authorises.
- To apply online via the agency’s website
- Provide your passport details and specify the entry port.
- Pay the service fee.
- Allow 2 – 4 working days for processing.
- You will receive the Vietnam Visa On Arrival Approval Letter by email, and a copy will also be sent to the Immigration Officers at your entry port.
- Print the Approval Letter and bring it to Vietnam with passport-size photos, your passport, and sufficient cash to cover the Vietnam Visa On Arrival stamping fee.
- Upon arrival, proceed to the Visa On Arrival counter at the airport to have your visa stamped into your passport.
- Pay the Vietnam Visa On Arrival fee
Read Related: How Overseas Vietnamese Can Register for Permanent Residence in Vietnam?
Processing Time and Duration of a Vietnam Visa
Processing Time of a Vietnam Visa
The processing times for a Vietnam Visa are as follows:
- eVisa: Approximately three working days
- Visa On Arrival, the approval letter typically takes 2 – 4 working days, although this may vary depending on the agency handling your application.
- Visa at an Embassy/Consulate: Timing varies by specific Embassy or Consulate.
Duration of a Vietnam Visa
Vietnam visas are granted for the durations listed below:
- Single-Entry Visa, valid for 1 month or 3 months
- Multiple-Entry Visa, valid for 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, or 1 year
The duration of your visa is contingent upon the purpose of your visit. For instance, tourist visas are generally for single-entry use, while work or business visas allow multiple entries and are valid for up to one year.
Once in Vietnam, if you possess a Vietnam Work Visa, you might be eligible for a Temporary Residence Card lasting up to 2 years.
The Investor Visa for Vietnam can be issued for a period of up to five years.
What is the Cost of a Vietnam Visa?
Visa costs for Vietnam are outlined below:
- For a Vietnam eVisa: US$25
- For a Vietnam Visa on Arrival:
- Single-entry, 1 month: US$25 stamping fee upon arrival (in addition to the service fee for the Letter of Approval)
- Multiple-entry, 1 month: US$50 stamping fee upon arrival (in addition to the service fee for the Letter of Approval)
- Single-entry, 3 months: US$25 stamping fee upon arrival (in addition to the service fee for the Letter of Approval)
- Multiple-entry, 3 months: US$50 stamping fee upon arrival (in addition to the service fee for the Letter of Approval)
- Multiple-entry, 6 months: US$95 stamping fee upon arrival (in addition to the service fee)
- Multiple-entry, 12 months: US$135 stamping fee upon arrival (in addition to the service fee for the Letter of Approval)
- For a Vietnam Visa application at an Embassy/Consulate: The fee varies depending on the particular Embassy or Consulate.
Read Related: An Overview of Common Visa Mistakes to Avoid When Traveling to Vietnam
“Can I Extend My Visa in Vietnam?” – Some Foreigners Ask
To remain in Vietnam after your visa expires, you must apply to a Vietnamese Immigration Office. You have two options:
- Apply for a Vietnam Visa Extension to prolong your stay under your current visa. The length of the extension will depend on your existing visa type. For example, a one-month visa can be extended for an additional month.
- Apply for a Vietnam Visa Renewal if you wish to change your visa category or if you entered Vietnam using the visa-exemption scheme.
Be aware that visa extension regulations are subject to frequent changes, so it is crucial always to consult the local Immigration Department office in Vietnam. Extensions may not be granted for some visa categories or individuals from certain countries.
Download the full PDF guide for the Vietnam Visa Guide now!


clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly






