Vietnam has emerged as the premier choice for electronics business globally in recent times. For example, Xiaomi Corp announced the commencement of smartphone production in Vietnam. In 2023, the electronics industry has encountered various opportunities and challenges due to cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and robotics. For investors looking to open a new company in Vietnam, the electronics sector presents a highly promising environment driven by innovation and strategic growth.
Vietnam embraces the 4.0 revolution but faces challenges, including supply chain disruptions, cybersecurity concerns, legislative restrictions, and global competition. Almost all electronic and telecommunications equipment in the hardware sector is imported, up to 99%. Mr. Nguyen Thien Nghia, the deputy director general of the Ministry of Information and Communications, asserts that the electronics technology industry has grown significantly in revenue, and most contributions come from foreign businesses.
Electronics Industry in Vietnam
In 2024, Vietnam’s electronics industry witnessed a remarkable boom, achieving an export turnover of US$126.5 billion, which accounted for one-third of the nation’s total export value, according to the General Statistics Office (GSO). Of the total, electronics and components exports soared to $72.56 billion, marking a 27% increase year-on-year. Meanwhile, exports of phones and components reached $53.9 billion, the GSO reported. The key destinations were China, the US, and South Korea. Notably, the country’s exports of computers, electronic components and phones to Europe and America exceeded $56.9 billion, contributing nearly 45% of the total export turnover.
The Vietnamese electronics market saw significant growth from 2016 to 2020, driven by a surge in foreign direct investment (FDI) projects. Industry giants like Samsung, LG, and Foxconn heavily invested in high-tech electronics manufacturing facilities during this peak period. The electronics technology sector claimed 35.7% of Vietnam’s industrial market share in 2017, which showcased its robust development.
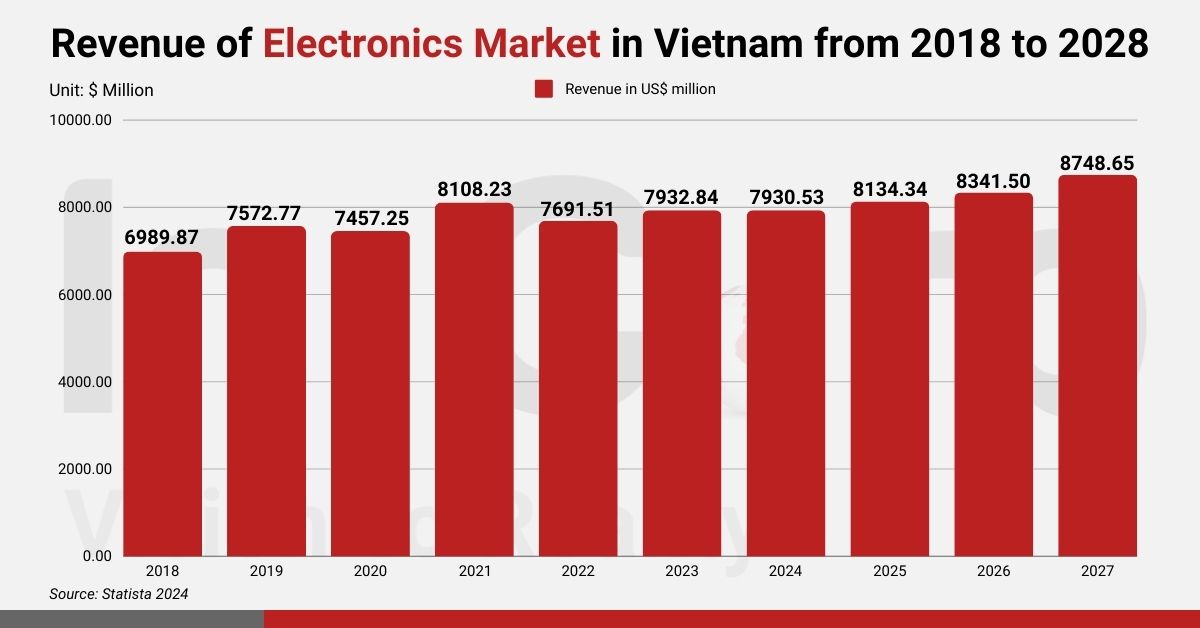
The country’s electronics market also faces challenges, notably its over-reliance on FDI. Statistics revealed that, in June 2022, only 26.72% of the ICT sector’s revenue was attributed to “Made in Vietnam” products. The expected worth was approximately US$19.4 billion, constituting a part of the industry’s total exceeding US$72.5 billion. This highlights a need for domestic businesses to foster originality and autonomy.
As per a report from the Industry Agency under the Ministry of Industry and Trade (MoIT), the export turnover surpassed US$114 billion, marking a 6% increase in 2022. This accounted for over 30% of the country’s total exports.
Investing in Vietnam’s Electronics Industry? Check out InCorp Vietnam’s business registration solutions
Current Trends in the Electronics Manufacturing Sector
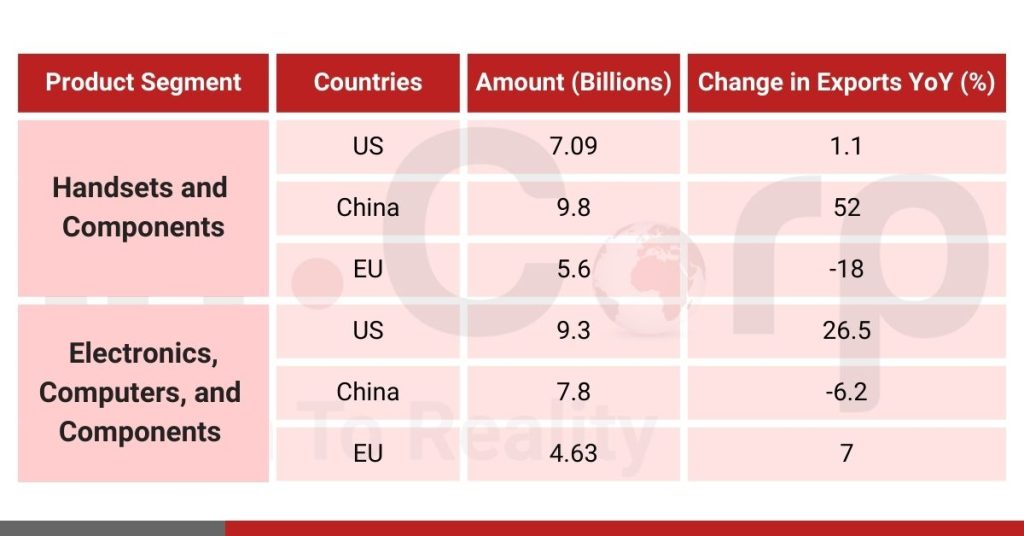
As the General Statistics Office reported, Vietnam’s electronics sector experienced a robust performance, achieving exports worth US$116 billion in 2021. Notably, Handsets and Components constituted a substantial portion, totaling US$57.5 billion. However, electronics, computers, and other components contributed US$50.8 billion, marking respective increases of 11.5% and 13.6% compared to 2020.
Samsung Electronics Group’s general director, Roh Tae-Moon, disclosed plans to commence mass production of transistor chip mesh at the Samsung Electronics Vietnam – Thai Nguyen facility in July 2023 following successful trial runs.
Similarly, Apple was poised to relocate a portion of its MacBook production to Vietnam by mid-2023. It diversified its electronics manufacturing base amid heightened technical tensions between the US and China. This strategic move aligns with Apple’s broader efforts to reduce reliance on Chinese production facilities.
In anticipation of technological advancements, Vietnam’s electronics business sector is poised for expansion, with forecasts extending to 2025. Technology dissemination is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, offering significant opportunities for growth and innovation.
As the world transitions to the era of 5G connectivity, Vietnam stands at the forefront of this technological shift. The rollout of 5G infrastructure promises to revolutionize connectivity, enabling the widespread adoption of
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- Internet of Things (IoT) applications
Vietnam is witnessing a surge in interest in smart home technologies, including intelligent lighting, security systems, and smart household appliances. This trend emphasizes the country’s readiness to embrace technological advancements and adapt to the changing preferences of consumers.
Some “Big” Electronics Business Manufacturers in Vietnam
Vietnam has become a hotspot for major technology companies, including Samsung, Foxconn, Canon, LG, and Intel. All of these companies have established factories across various provinces, such as:
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Capital of Vietnam (Hanoi)
- Bac Ninh
- Bac Giang
- Hai Phong
- Thai Nguyen
Read More: Vietnam’s Industrial Zones: A Key Player in Global Manufacturing
Foxconn recently announced a substantial investment of US$270 million in Bac Giang to produce iPads and MacBooks for Apple. It is also planning to invest US$40 billion in Vietnam within the next three to five years. Lenovo and Apple’s primary partners, including Luxshare, Wistron, Pegatron, and Foxconn, are actively increasing their electronics manufacturing activities in Vietnam.
Samsung’s Electronics Vietnam Thai Nguyen (SEVT) has been a key contributor to Vietnam’s electronics industry, shipping 925 million phones in a decade and providing jobs for over 150,000 people.
Other major players like Apple, Dell, Pegatron, OPPO, HP, and Bose are considering relocating production plants to Vietnam. Additionally, both Korean companies, Samsung and LG, are planning substantial investment increases, with the former aiming to raise its investment to US$20 billion and the latter planning an additional injection of US$4 billion in Vietnam.
These developments underline Vietnam’s emergence as a crucial global technology and electronics manufacturing hub, driven by lower labor costs, stable currency, and favorable tax incentives. As technology giants continue to expand their presence, Vietnam’s electronics industry is positioned for sustained growth, making significant contributions to the country’s economy.
The Move of Chinese Electronics Manufacturers to Vietnam
Chinese manufacturing firms are increasingly setting up factories in Vietnam to mitigate risks and overcome trade barriers. Gongjin Electronics, for example, has invested nearly CNY400 million in building its factory in Vietnam, which now fulfills all its international orders.
Similarly, DBG plans to hire and train around 15,000 workers in Vietnam and establish a comprehensive industrial chain supporting local procurement in Thai Nguyen province. This reflects the trend of Chinese companies expanding operations into Southeast Asia, particularly in regions like the Red and Mekong Rivers.
This shift signifies Vietnam’s growing appeal as a manufacturing destination, offering stability and opportunities for companies seeking to diversify their production base outside China.
Read More: Moving to Vietnam for Chinese Businesses: What are the Benefits?
Why are Chinese Electronics Manufacturers Choosing Vietnam?
Vietnam emerges as a compelling alternative to China for manufacturing, driven by geopolitical diversity, financial advantages, and infrastructure development. Due to factors such as tariffs and China’s “zero-COVID” policy, companies are diversifying their production away from China.
Financially, Vietnam presents favorable conditions, including stable currency and lower labor costs than China. With the market labor rate roughly 1/3rd of that in China, this country remains hungry for foreign investment, offering significant tax incentives to attract businesses.
However, a challenge lies in the educational qualifications of the workforce, with only 22% holding certifications. The government is strategically investing in public education, which is evident in increased spending to boost enrollment and maintain high academic standards. It will contribute to Vietnam’s competitive edge in global rankings.
Vietnam’s infrastructure is rapidly evolving, with investments in port facilities, highways, and public transportation projects. The public transportation initiatives aim to alleviate traffic congestion in cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, fostering a conducive business environment. The government prioritizes infrastructure development to sustain the country’s status as a manufacturing hub. Major efforts are underway to enhance efficiency and scope through foreign and private investment.
Furthermore, Vietnam offers lucrative tax incentives to foreign-invested companies, including a 10% Corporate Income Tax (CIT) rate applicable for 15 years in various economic and high-tech zones. Notable companies like Inventec, TCL, and Apple have relocated production from China to Vietnam, with others planning similar moves, including Microsoft and Lenovo.
Find more about Corporate Income Tax in Vietnam Infographic from InCorp Vietnam
Opportunities for Electronics Manufacturers
Vietnam’s liberalized market policies and worldwide engagement foster a favorable investment environment across diverse sectors. Investors can capitalize on Vietnam’s dynamic economy and its efforts to integrate into the global market, ensuring sustainable returns and long-term success.
Liberalization in Trading
Investors eyeing Vietnam can benefit from its extensive network of FTAs facilitated by its ASEAN membership. The EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA) significantly reduces import tariffs, previously averaging 8.9% for non-EU countries. However, adherence to rules of origin in FTAs is essential. Vietnam’s import-dependent electronics industry (EI) faces challenges due to underdeveloped supporting industries, hindering domestic firms’ integration into global value chains.
Read More: The Definitive Guide to Vietnam’s 16 Active Free Trade Agreements (Updated August 2023)
Tax Advantages
Investors in Vietnam benefit from reduced tariffs and corporate income tax (CIT) breaks. The government offers tax incentives for companies operating in high-tech sectors, high-tech zones, specific industrial zones, and underdeveloped socio-economic regions.
New foreign-invested companies in the high-tech sector can benefit from a reduced tax rate of 10% for the first 15 years and then 17% for the following 10 years. Investors may also enjoy extended tax relief when making their initial investment. For instance:
- Investors qualifying for the 10% CIT rate may benefit from a four-year tax exemption followed by a nine-year 50% reduction.
- Those operating in specific areas are entitled to a four-year tax exemption and a five-year 50% reduction.
- Investors operating in designated areas or industrial zones can receive a two-year tax exemption and a four-year 50% reduction.
- In R&D projects, 10% of annual profits can be allocated to a tax-deductible fund before tax assessment.
Government Reforms
Vietnam’s government has prioritized electronics, information, and telecommunication technologies for industrial development from 2025-2035. Foreign investors are urged to join designated Electronics Industry (EI) clusters and industrial zones, potentially qualifying for CIT breaks.
Suitable Demography
Vietnam has entered a “golden population” age from 2010 to 2040, where the working-age population surpasses its dependents. With a minimum wage ranging from US$140 to US$202 across regions, Vietnam offers relatively low labor costs compared to its regional counterparts.
Vietnamese engineers in the electronics industry demonstrate high qualifications, contributing significantly to global software development. According to the World Bank’s STEP Skills Measurement Program survey, junior staff training and educational quality remain areas of concern.
Read Related: Vietnam’s Workforce: High Demand Skills and Advice for Business in 2024
Challenges for Electronic Manufacturers in Vietnam
In 2023, Vietnam’s electronics technology sector faced significant challenges due to fierce competition from international firms. The sector prioritizes employee innovation, adaptability, and commitment. Ensuring timely delivery and maintaining high-quality standards adds pressure to companies.
Besides, there are other challenges faced by the country’s electronics industry.
Absence of Electronics Industry Clusters
Economic clusters include suppliers, infrastructure, and research institutes providing specialized services. These are emerging in industrial provinces like Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, and Haiphong.
The strategic cluster location allows enterprises to offer cost-effective products and services without compromising timelines, fostering the generation of skilled labor and goods. This facilitates the transfer of knowledge and expertise and encourages collaborative efforts, ultimately promoting competitive advantages for all involved parties.
Dependence on Foreign Technologies
The Mobiistar Prime X-Max (Mobiistar Company) and the Bphone (Bkav Technology Group) entered the Vietnamese smartphone market between 2015 and 2016. However, both companies ceased operations after a brief period of activity.
Other reasons are:
- Intense competition emanated from major market players like Nokia, Samsung, LG, and Apple.
- Inadequate infrastructure and a limited understanding of Vietnamese consumers’ preferences.
Scarcity of Labor Resources
A study by the Ministry of Labor, Disabled and Social Affairs and the GSO in 2018 revealed Vietnam’s working population stood at 55.12 million. Only 22% possessed vocational education and certification, highlighting a deficiency in trained personnel.
Educational institutions suffer from understaffing, complicating the recruitment of junior employees. Enhancing vocational training could boost national productivity and competitiveness, effectively addressing the country’s skilled labor shortage.
Read Related: 10 Key Obstacles to Doing Business in Vietnam
Conclusion
Vietnam, Southeast Asia’s fastest-growing economy, holds a strategic geopolitical position near China. Amid the China-US trade conflict, numerous EU companies are shifting their manufacturing operations here. As businesses seek stability amidst global uncertainties, Vietnam emerges as a prime destination for investment and production. Its dynamic growth and trajectory positions make it a pivotal player in the evolving global trade and commerce landscape.

clients worldwide

professional staff

incorporated entities in 10 years

compliance transactions yearly
Learn the Right Setup for Business
Expansion in the Vietnam
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Manufactured In Vietnam
- Vietnam manufactures a wide range of products, including electronics, textiles, garments, footwear, furniture, and machinery. It is also a major exporter of agricultural products like coffee, rice, and seafood.
Where To Buy Electronics In Vietnam
- You can buy electronics in Vietnam at major retailers like Nguyễn Kim, Điện Máy Xanh, and MediaMart. Online platforms such as Tiki, Lazada, and Shopee also offer a wide selection of electronics.
What are the 4 types of FDI?
- The four main types of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) are: 1. **Horizontal FDI** – An investor sets up the same type of business operations in a foreign country as it operates in its home country. 2. **Vertical FDI** – A business invests in a foreign country to control stages of its supply chain (e.g., sourcing materials or distributing products). 3. **Conglomerate FDI** – An investor starts a business in a foreign country that is unrelated to its existing operations. 4. **Platform FDI** – A company invests in a country to use it as a base for exporting to a third market. Each type reflects different strategic objectives and levels of integration with the foreign market.
What is the FDI situation in Vietnam?
- Vietnam continues to attract strong foreign direct investment (FDI) due to its stable political environment, competitive labor costs, and numerous free trade agreements. In 2023, total registered FDI reached over USD 36 billion, with manufacturing, real estate, and energy among the top sectors. Key investors include countries like Singapore, South Korea, Japan, and China. The government actively supports FDI through tax incentives and improving administrative procedures.






